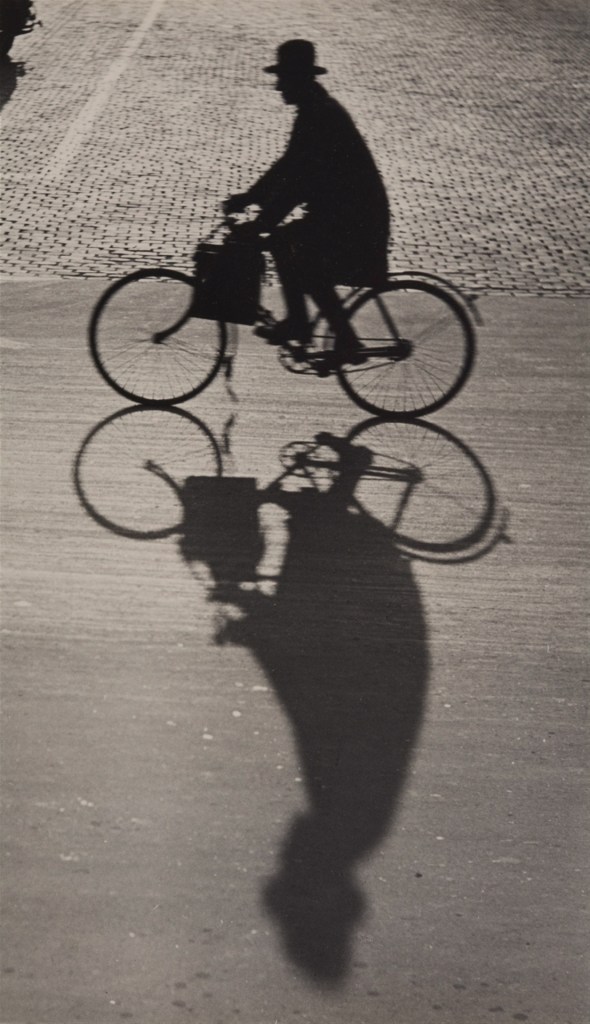
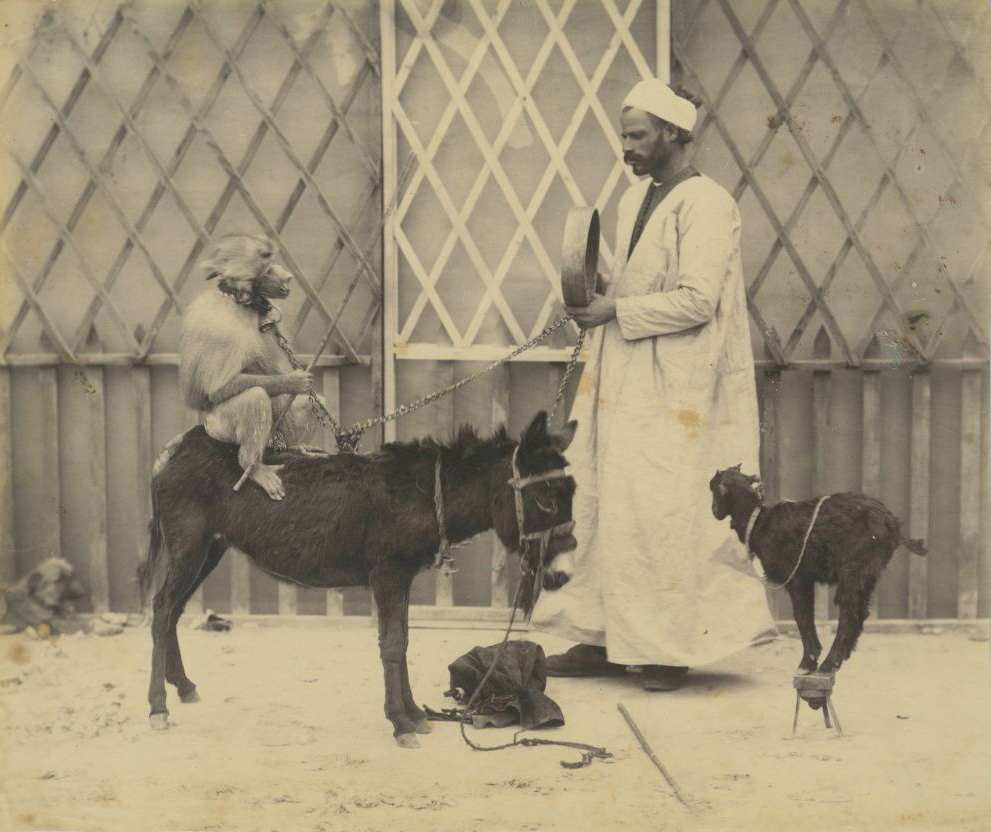
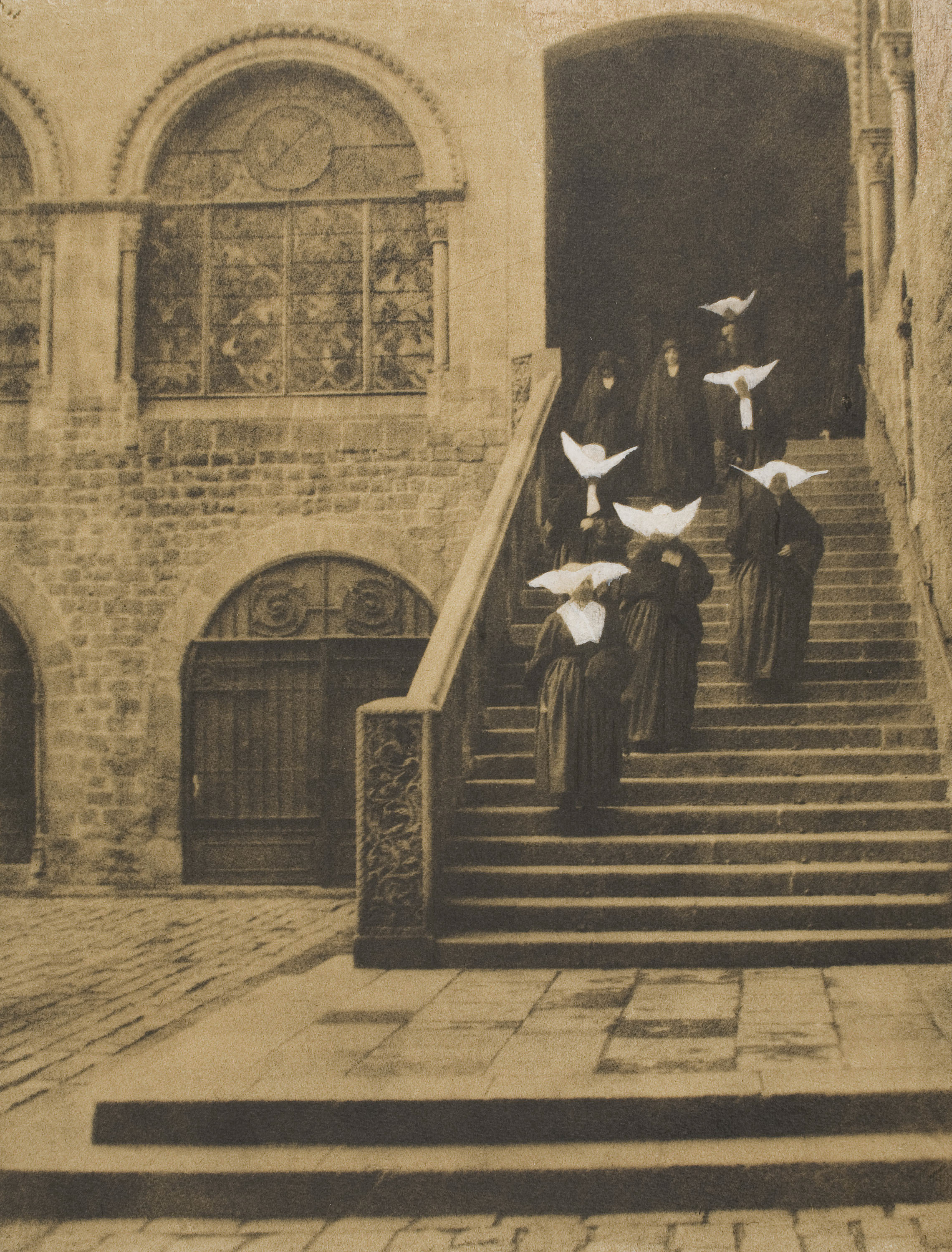
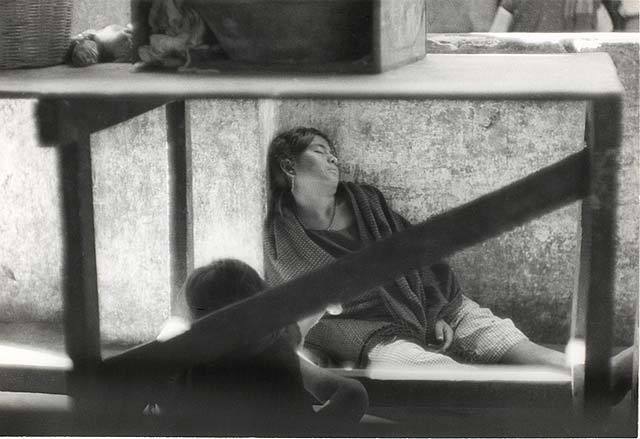
Girl holding a cat · 1945

images that haunt us


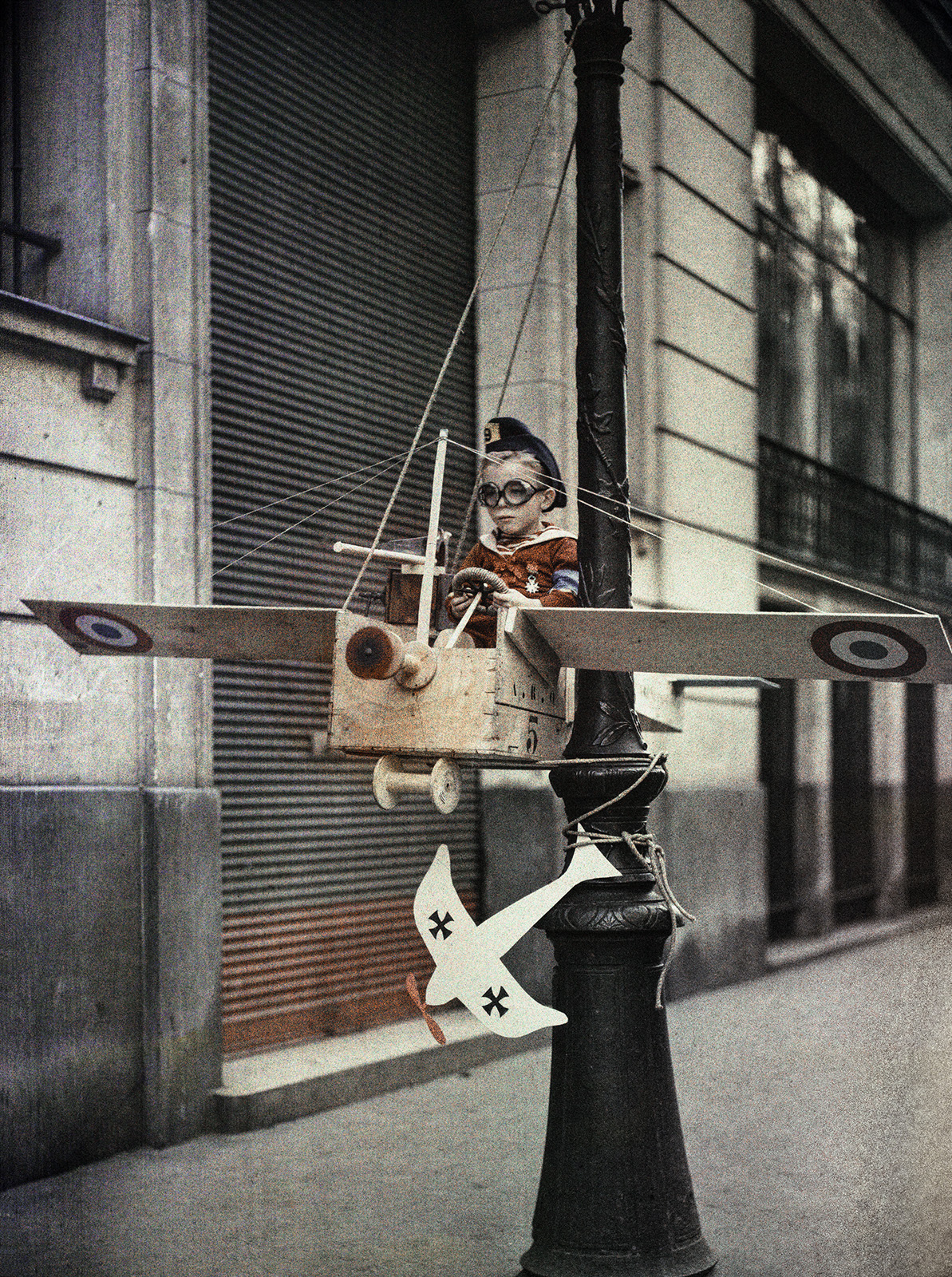
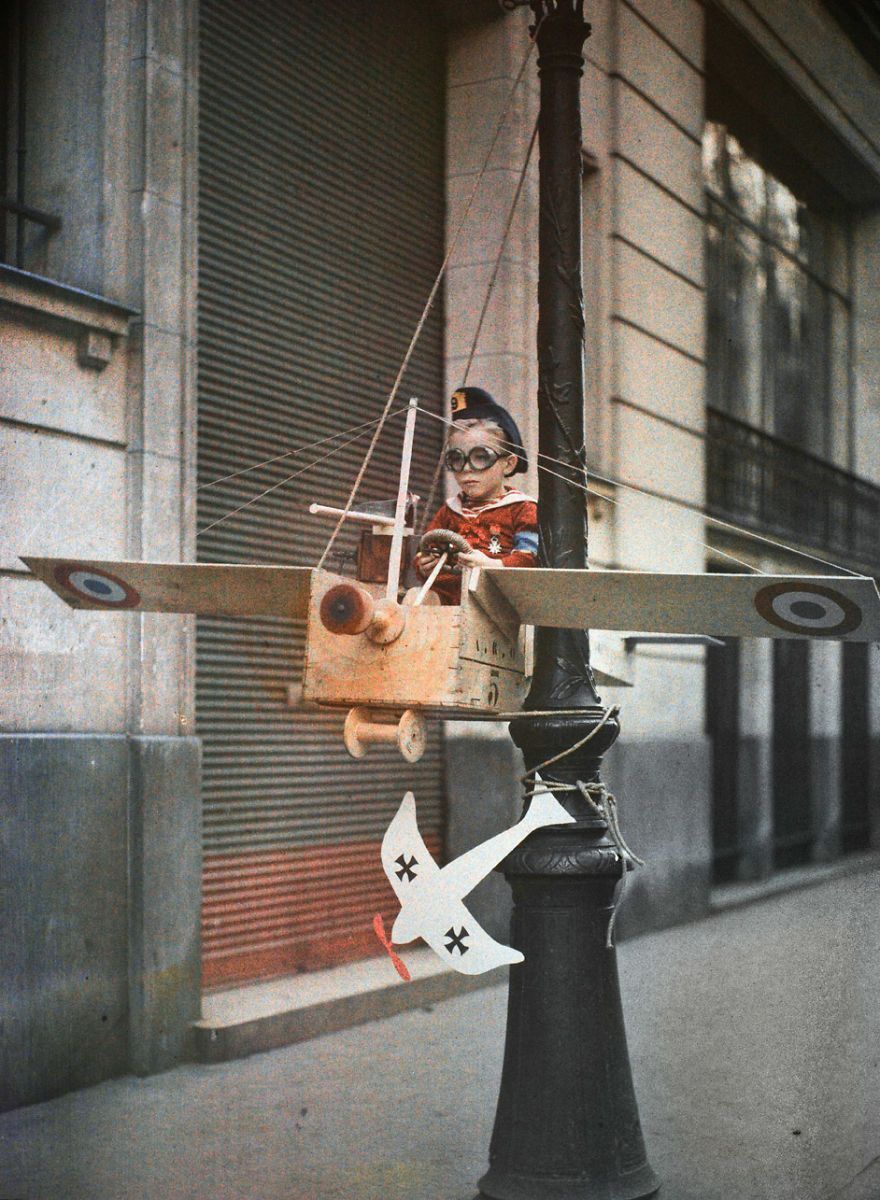
In 1915 Gimpel befriended a group of children from the Grenata Street neighborhood in Paris who had established their own “army”. He began to visit them regularly on Sundays, helping them to build their arsenal from whatever was to hand, providing direction in “casting”, and recording with his camera the army’s triumphs over the evil enemy, the Boche.
Gimpel was charmed by these children and came to know each of them well: the “chief”, the eldest in the garrison; his friend, who was conscripted to play the unenviable role of the Boche; and Pépète, who was “small, slightly misshaped, rather scrofulous, looking somewhat like a gnome” but who nonetheless played the part of an ace aviator. At the end of each session, Gimpel would reward the troops with barley sugar, causing all to shout with one voice, “Long live the photograph!”
quoted from Luminous-Lint online exhibition : Autochromes and Autochromists of WWI

From : La guerre de gosses, Léon GIMPEL, Paris, 1915
More images at Images en ligne de la Société française de photographie (SFP)
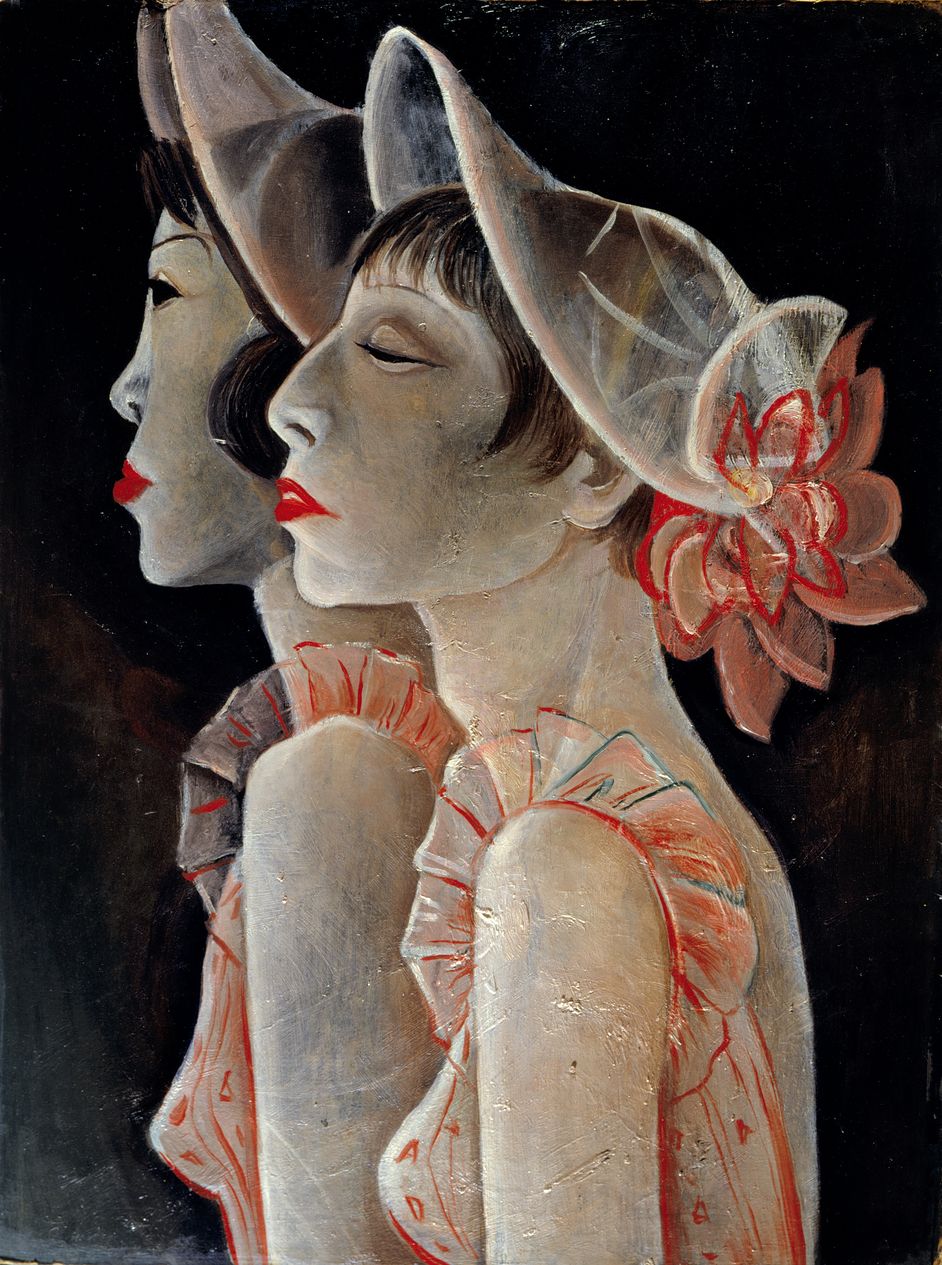

In the pleasure-hungry Berlin of the 1920s, theatres vied for attention with spectacular variety shows. Chorus girls in scanty costumes provided an erotic touch. As links in the chain of swinging legs, they were usually depicted as a type, not as individuals. But the two women in “Chorus Girls” by Jeanne Mammen (1890–1976) could hardly be more different. The artist centres on their weary faces, sallow skin and garish lipstick. The real attraction – the dancers’ long-limbed bodies – are only visible down to the breast. They pause for breath, no trace of glamour here.
Mammen, a free-lance artist and a prototype of the emancipated “New Woman”, often highlighted female clichés of the day. The chorus girl in front has the facial features of the artist. The figure behind resembles her sister Mimi. [quoted from Berlinische Galerie]

Weimar Clubs and cabarets – German cities, 1920s
After the collapse of its Empire and the defeat of the First World War, Germany became a democracy, the Weimar republic. In the early 1920s, people yearned for excitement, there was a sense of liberation and the economy started to recover. Night clubs appeared which fused cabaret, literature, art, music, theatre and satire in multi-sensory experiences. American jazz and dance crazes including the foxtrot, tango, one-step and Charleston became popular and exotic dances by Anita Berber, Valeska Gert and famously Josephine Baker were performed.
Fantasy spaces were created such as the dance-casino called Scala where the ceiling was sculpted into jagged structures that hung down like crystalline stalactites. The pulsating energy of such clubs and bars was captured by artists including Otto Dix, Jeanne Mammen and Elfriede Lohse-Wächtler.
[Barbican Centre] From Into the Night: Cabarets & Clubs in Modern Art (October 2019 to January 2020)


Visions of a dark world in the art of Weimar Germany [Apollo magazine]
Review on the exhibition Magic Realism: Art in Weimar Germany 1919-33 (Tate Modern, 2018-19)
[…] towards the end of the exhibition, a small cluster of drawings introduces the work of Jeanne Mammen. Mammen’s drawings – gauzy depictions of women in watercolour, pen and ink – illustrated fashion magazines and poetry publications throughout the 1920s, until the Nazis shut down the journals she worked for and she went into inner exile, refusing to show her work. Here, they fill an important gap in describing women’s experiences of city life. Mammen observed women on the streets of Berlin and in nightclubs, and often depicted them in conversation, smoking, or playing cards. In Brüderstrasse (Free Room) (1930), the women are intimate and aloof; in Boring Dolls (1929), they’re defiant, out for their own pleasure.
[…] The exhibition doesn’t quite tease out the paradoxes between trauma and humour, leaving both to loiter in the murkiness of Dix’s circus tent. What we’re given is a vision of a world that hinges on reality yet twists from view. It’s a distortion of the truth, full of landscapes littered with war debris and nightclub corners filled with smoke. It’s the same world, but darker than before.
quoted from the review by Harriet Backer for Apollo magazine