

images that haunt us



Titelbild / Die Bühne, Heft 242, Juni 1929 : Drei Tanzende Wienerinnen. Hansi Koch, Loli Petri und Frauke Lauterbach, alle aus der Bodenwieser-Klasse. Sie tanzen einen der modernen Ausdrucks- und Bewegungs-tänze. Foto: Feldscharek
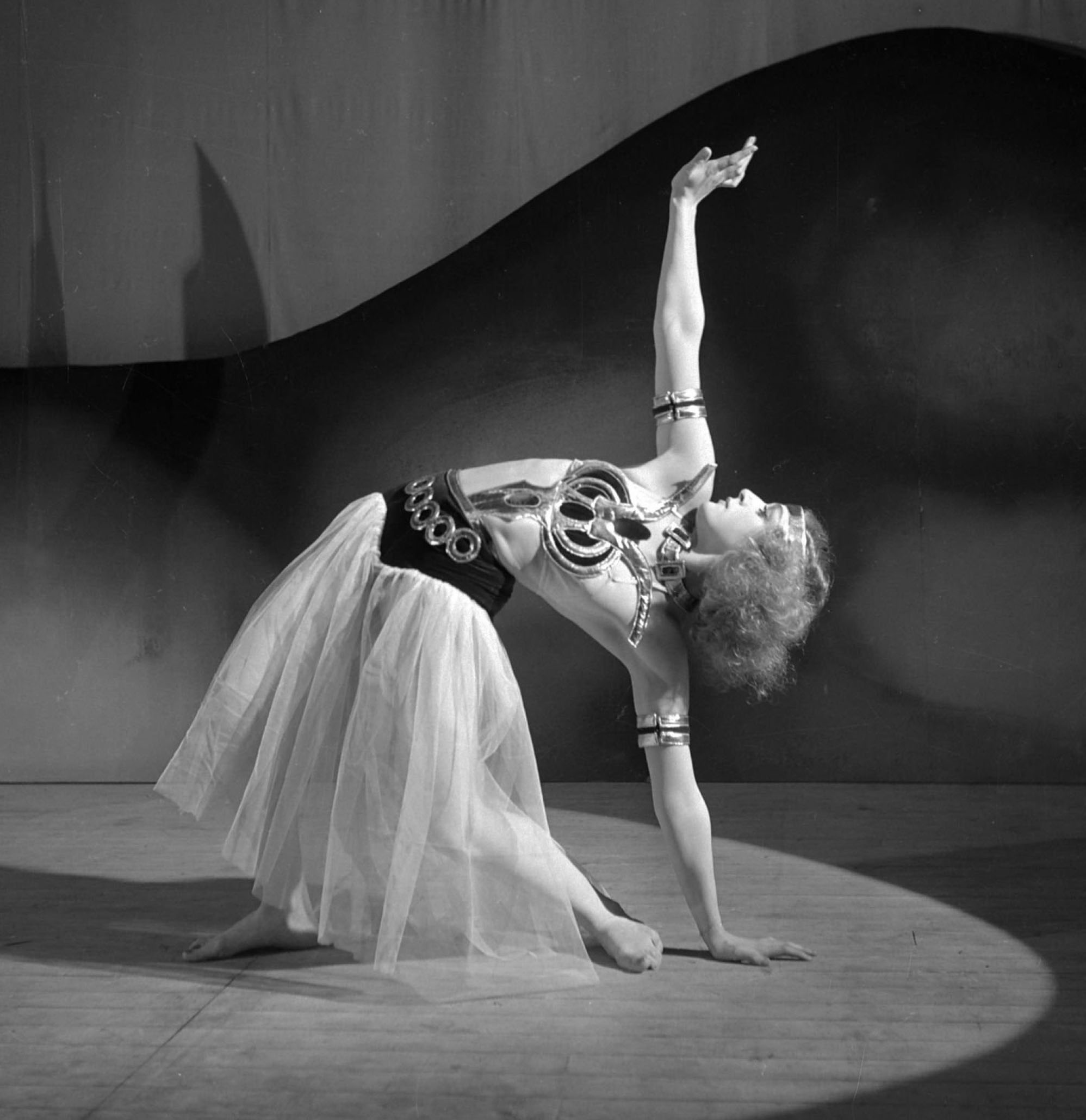


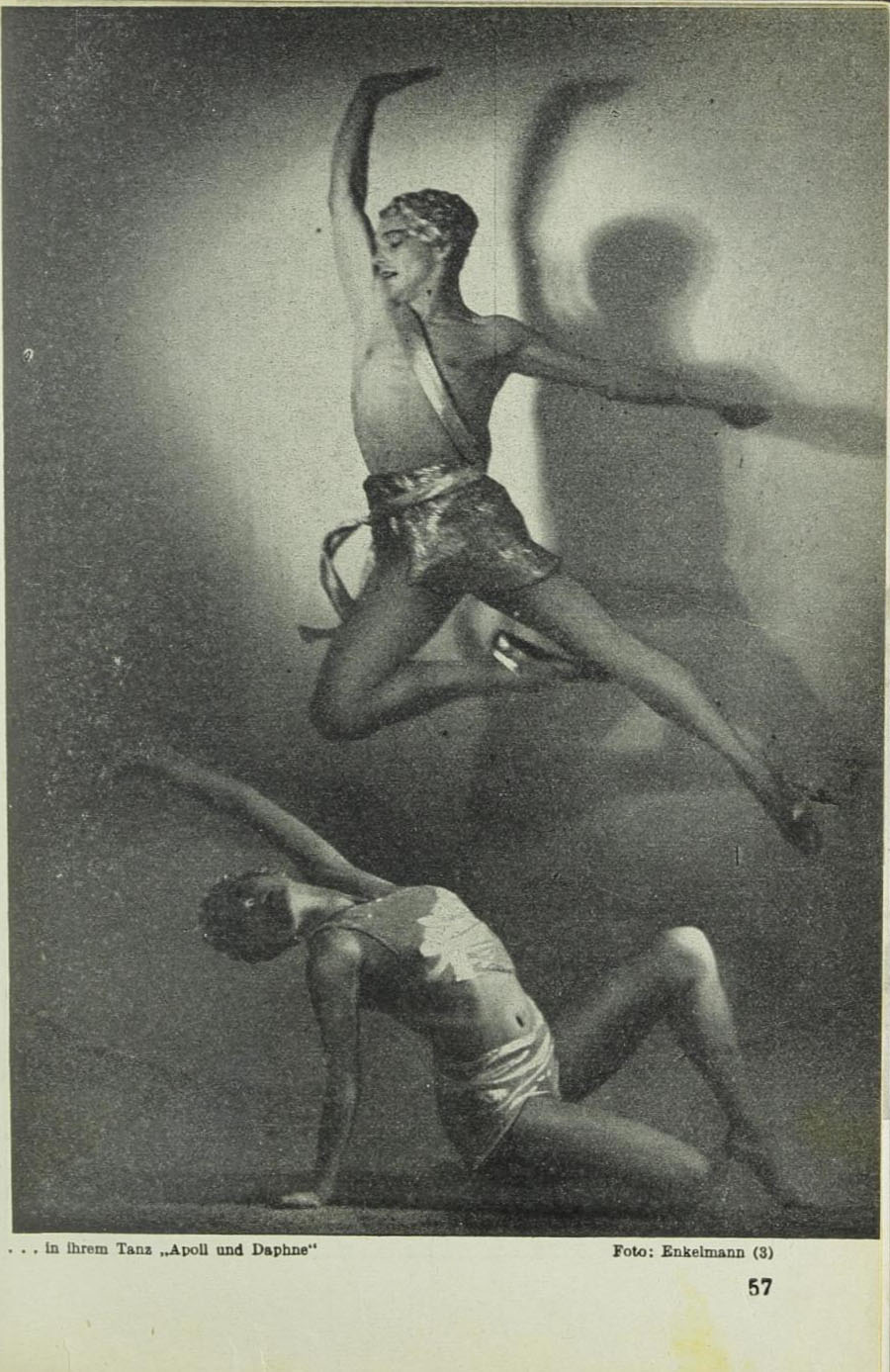







The images above are part of the exhibition: «Dansen har mycket gemensamt med arkitektur» / «Dance has a lot in common with architecture» (2013)
Arkitektur- och designcentrum / Center for Architecture and Design (Ark Des)
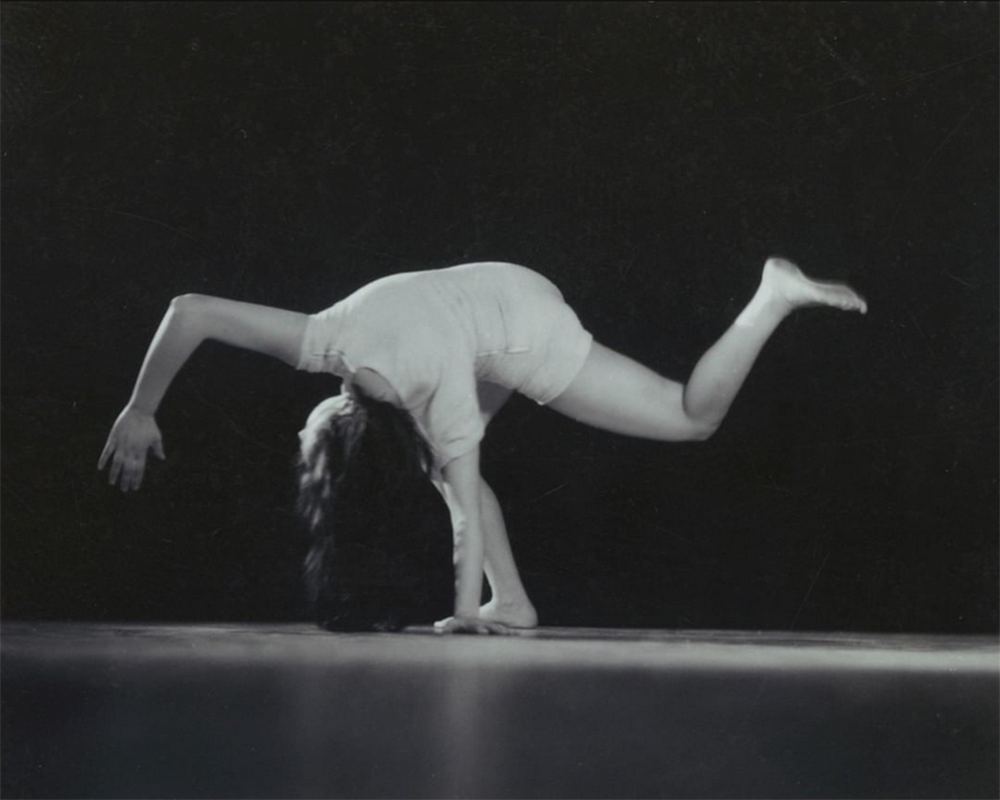


Both images above this line are uncredited in source: Dansmuseet (view post in this blog : Birgit Åkesson training), but we reckon that them could belong to the same photo-session with Sune Sundahl














All the images in this post are from the exhibition: «Dansen har mycket gemensamt med arkitektur» (2013). Some of the images are dated 1939-1947 and most of them undated.
«Dance has a lot in common with architecture» (2013)
Movement, rhythm, space and body in dance have much in common with architecture. Spatiality can only be experienced with the body, in movement. There are several good reasons to pay attention to the connections between the room shape and people’s movements in the rooms. Whether dancing or walking around a building, there is both flow and embodiment. Perhaps it was precisely these common denominators that made Birgit Åkesson choose the architectural photographer Sune Sundahl to document her early choreographies?
Photographing movement is a big challenge, a movement in a frozen moment can easily turn into a rigid pose without context or dynamism. In Sundahl’s collection there are, among other things, pictures from Birgit Åkesson’s own performance Blue Evening from 1946. The title was probably taken from the blue-painted Konserthuset in Stockholm, designed by Ivar Tengbom 1924-26. Here, Birgit Åkesson experimented with movements without music, which was unique for the time. She also studied during her lifetime the dances of other cultures, including dances south of the Sahara in Africa and the Butoh dance from Japan.
The dancer, choreographer and dance researcher Birgit Åkesson (1908-2001) taught the viewer to listen to the sound of movement in the silence. It was about holding a dialogue, where the rhythm carried the form that left invisible traces in the air. Birgit Åkesson started her dance career in the 1920s and 30s when she studied with the German-born choreographer Mary Wigman. It was from her that the Swedish dancer found the expressionist language, the free dance. Birgit Åkesson was one of the leading avant-garde artists in free dance.
Lenita Gärde, Center for Architecture and Design (quoted from ArkDes)














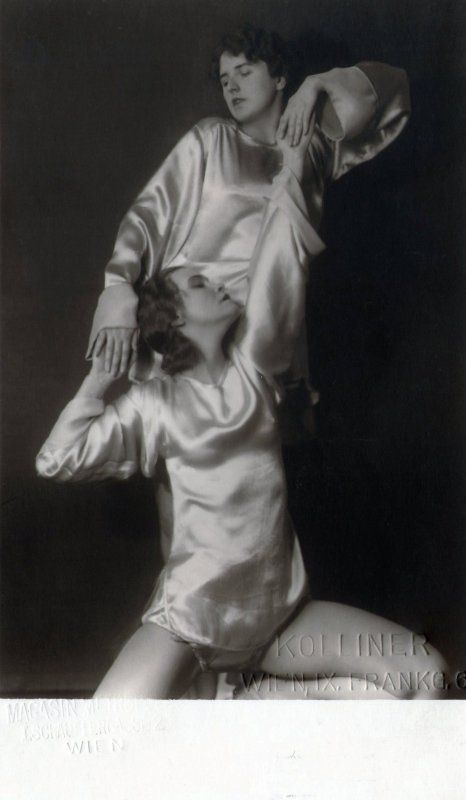
Photographer’s stamp with address at “Wien I. Ebendorferstraße 3”, her copyright stamp and her re-order stamp with handwritten negative no. “281” in ink, and handwritten title in pencil on the reverse [‘Die Tänzerin Ronny Johansson’]. Ronny Irene Johansson was born 1891 in Latvia, to Swedish and Scottish parents. Her father, a businessman in the shipping industry, sent Ronny to Russian and Swedish boarding schools. It was in Sweden that she established a professional dancing career, debuting in Weisbaden in 1916. After touring and performing throughout Europe, she moved to the USA in 1925 to pursue Modern dance. [quoted from source]
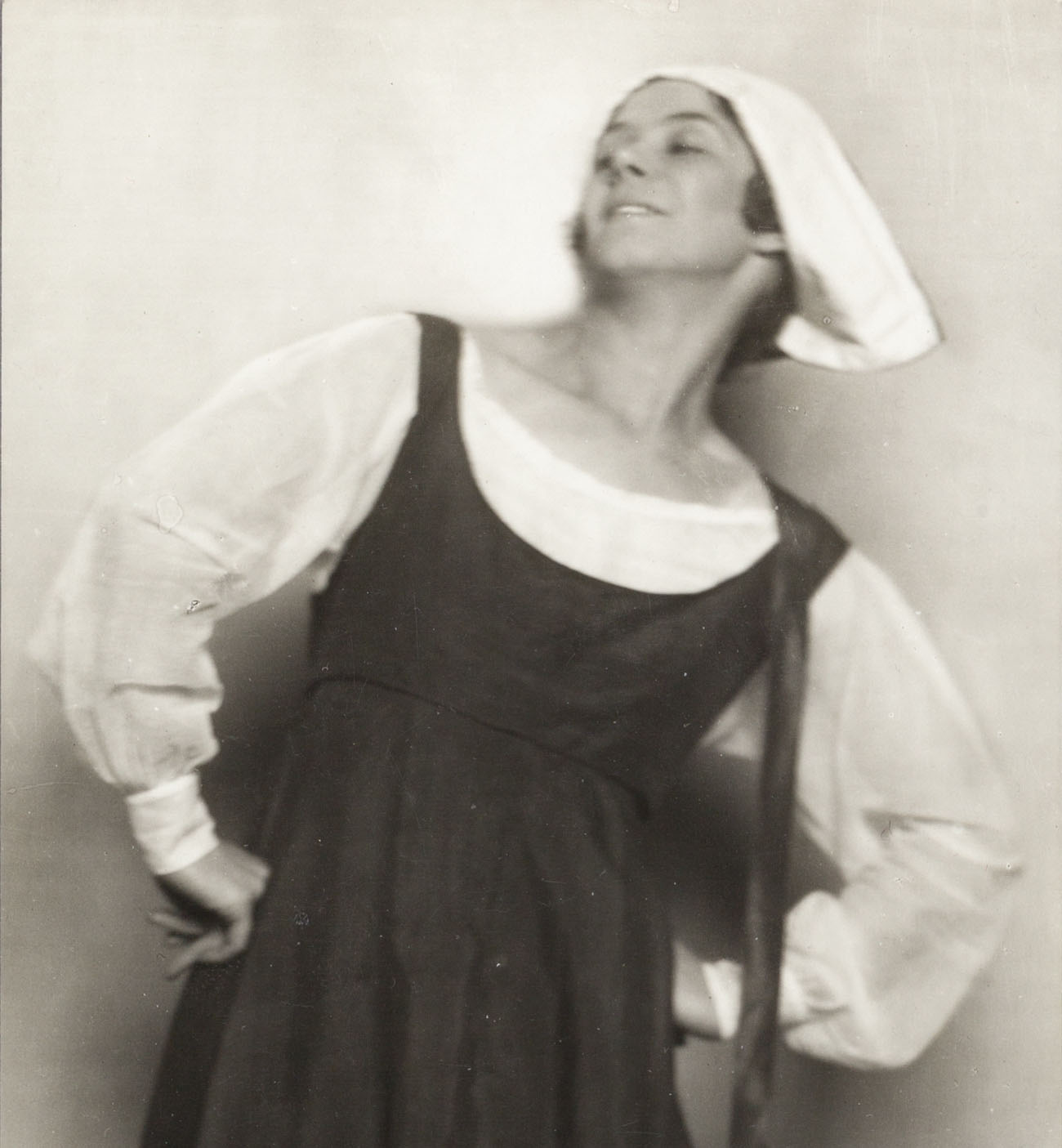
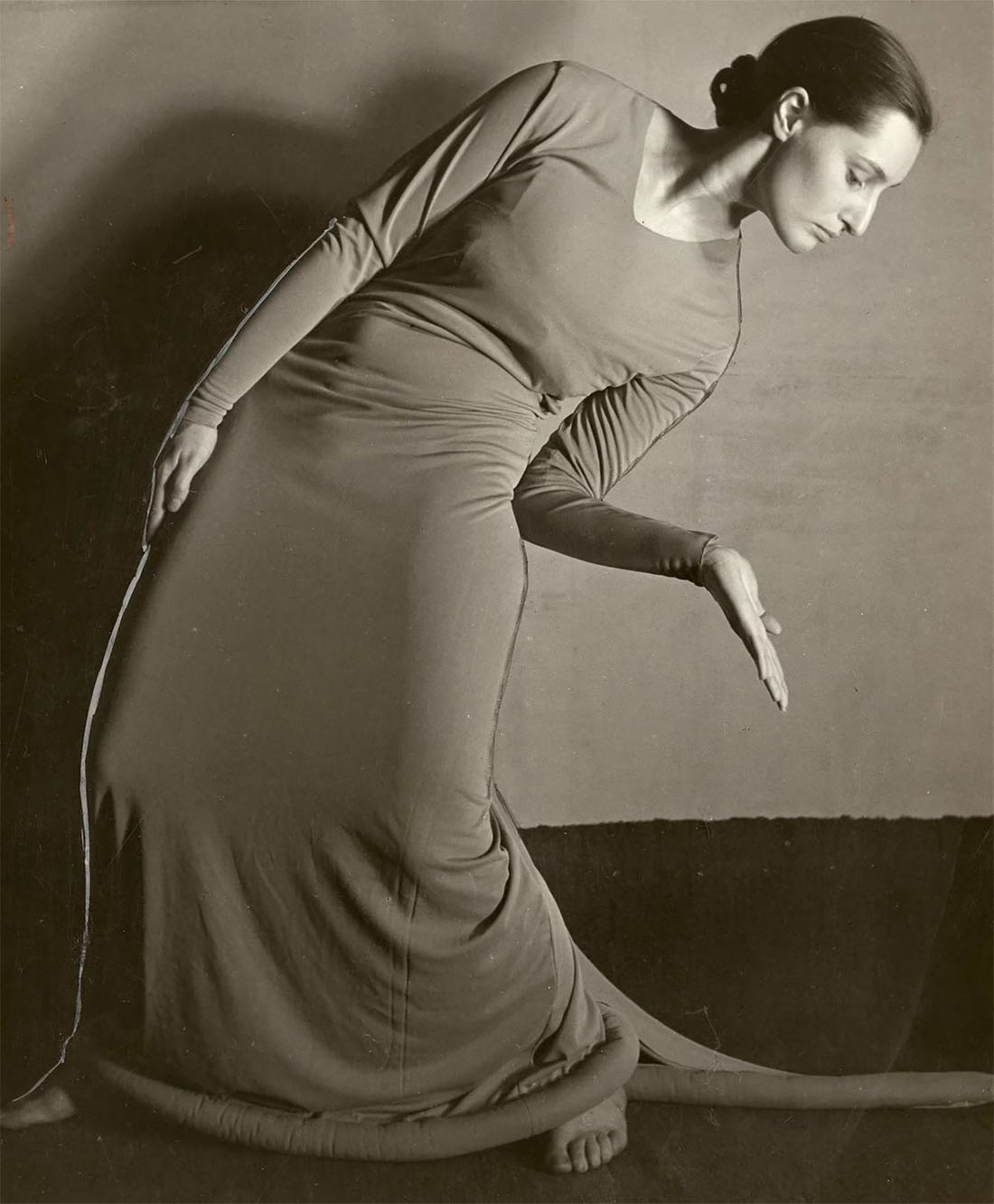


Eleanor Buchla (1910–1972) the first local dancer to gain a large audience, who began, c. 1931, performing her own choreography. Buchla’s dances, reportedly acclaimed by dance critics throughout the country, were a mixture of modern dance and Hungarian folk dance. She was the featured performer at the State of Ohio’s first dance symposium, hosted in 1933 by Ohio University, that drew students and devotees of modern dance from Ohio State, Wesleyan, Oberlin, Cincinnati, Kent State, the University of Virginia and the City of Detroit. Set to the music of Debussy, Chopin, Kodaly and the beloved Hungarian violinist and composer Jenö Hubay (1858–1937), her dancing evoked for Athens critic Forest Hopkins by turns the simplicity of Greek sculpture and the “severe and stylized [spirit of] Egyptian art. In some art circles,” said Hopkins, “Miss Buchla’s dancing is called modern, perhaps because of its free use of the entire body, particularly the torso, yet it is classic in conception. It carries refinement of form and simplicity of design molded successfully with the music.” She had studied ballet as a young girl and then in the late 1920s discovered modern dance.
“Buchla’s work as a whole merits high praise,” Cleveland Plain Dealer music critic Herbert Elwell wrote, “and there is no doubt about her success in her concert here, for the spectators lingered in their seats and clamored for more.” He praised “the subtle grace, the objectivity, the persuasive and suggestive immobility characteristic of [her] style.” Her physical beauty evoked for him “classic models,” while her arresting “personality made what she does seem important and interesting. Her dancing is sculpturesque in slow motion, and a sense of beauty is created in every line, which shows grace of movement. The impression at any moment is one of sculpture liquified and flowing with life.”
A strong proponent for dance in the schools, Buchla not only opened Cleveland’s first modern dance studio but also began a dance curriculum in the city’s summer playgrounds. She provided the choreography (and directed a number of productions) for several area theaters, including the Hudson Players, the Peninsula Players and, for six years, Cain Park in Cleveland Heights, and was instrumental in cultivating the first
Modern Dance Association, which was founded in 1934. An interesting footnote: Buchla was the sister-in-law of celebrated Cleveland artist Kalman Kubinyi. In the 1960s she and her husband Julius Kubinyi joined other Ohio families in providing temporary homes for Hungarian refugees in the wake of the uprising against the communist government. Though both Eleanor and Julius were born in America, they learned Hungarian from their parents and visited Hungary. In 1943 she played a key role in founding the Peninsula Library, on whose board she served until shortly before her death in 1972. / quoted from past masters project
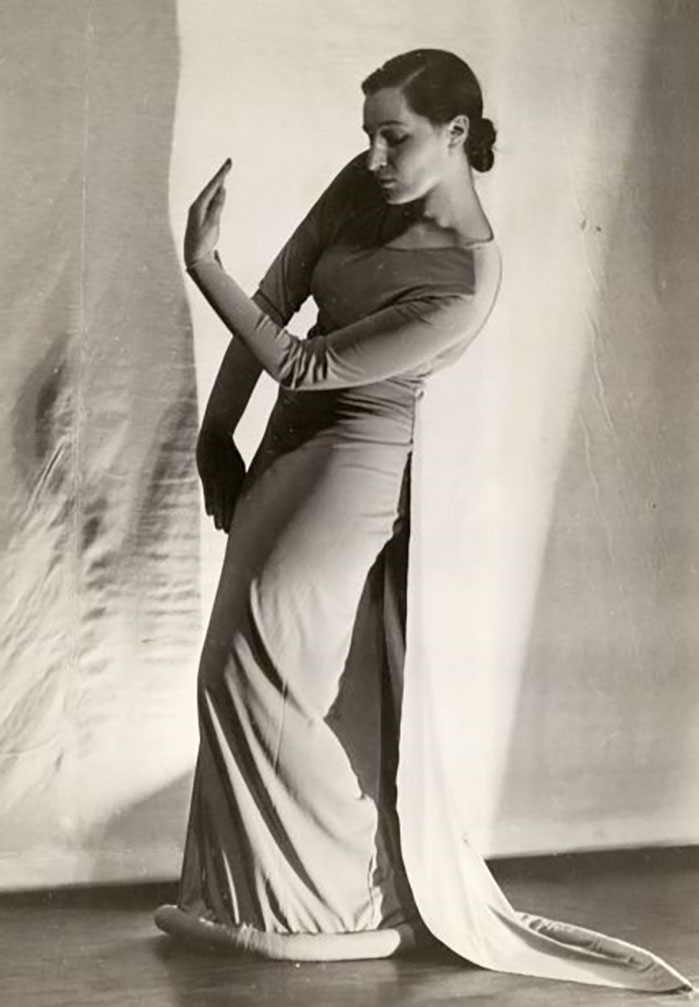
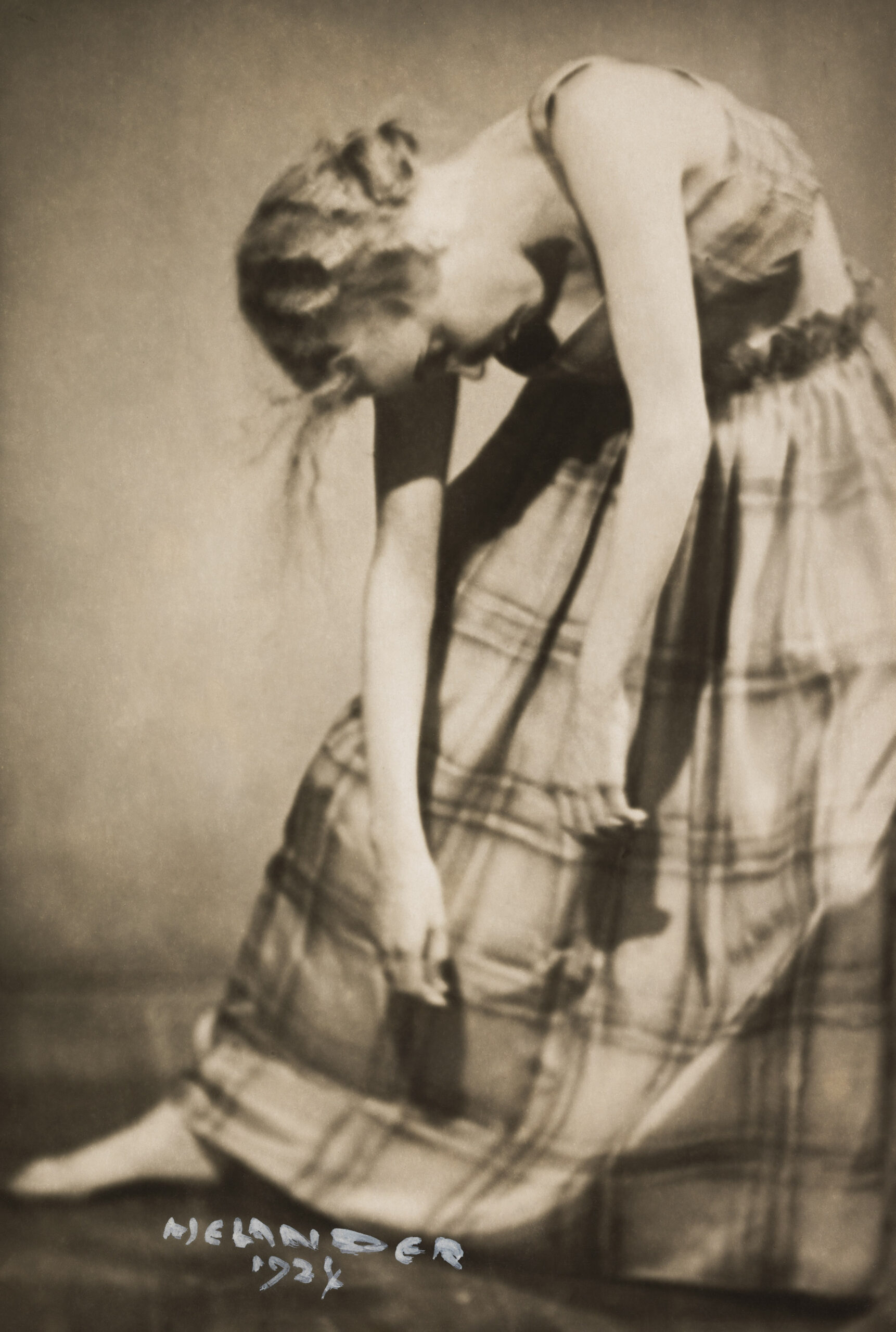




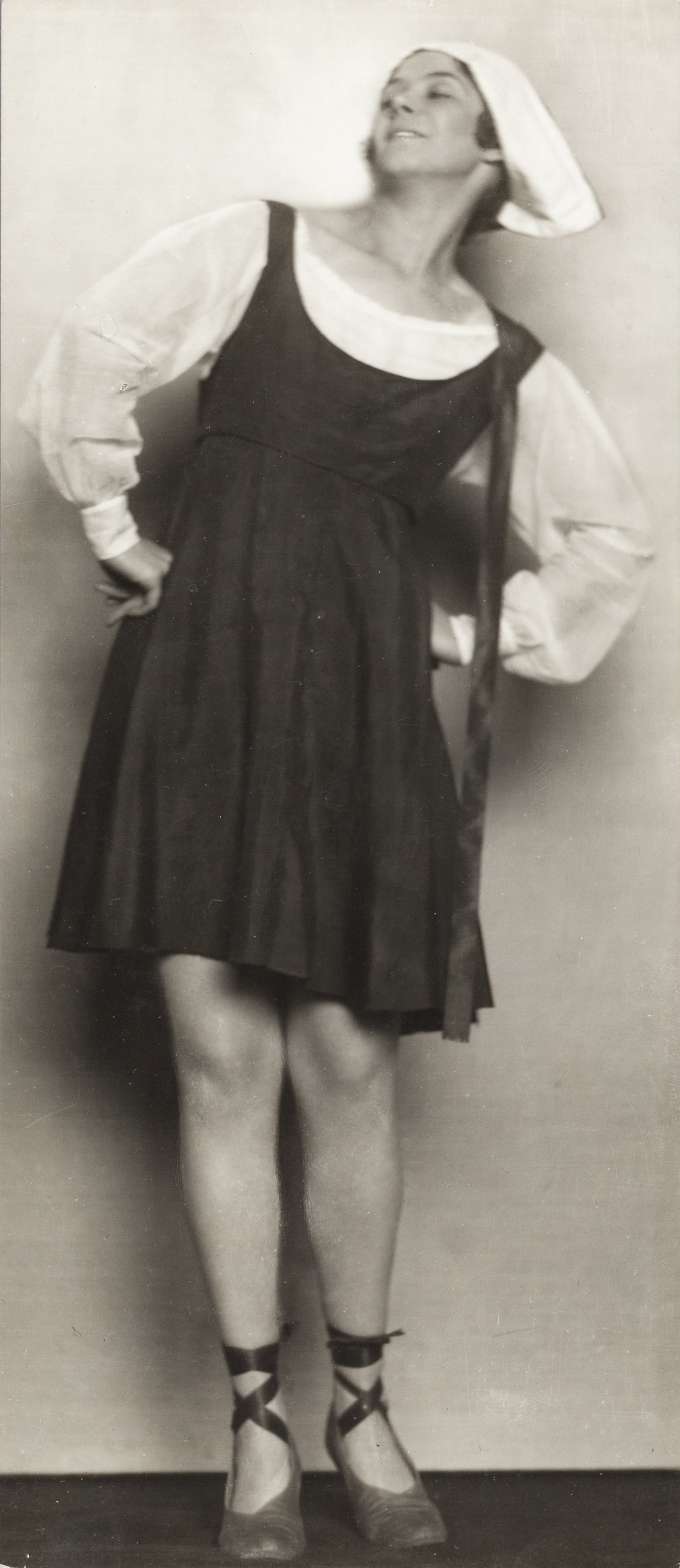
Bröyer, one of the pioneers of modern dance in Finland, created her own controversial style, bröyerism, or Bröyer-style in the 1920s and 1930s, in which dance was accompanied only by poetry recitation, an art form that, in it’s time, had a conflicted reception.
From: Poem – Vision – Flush: A dancedramatic series & Poem – Vision – Intoxication: A dance drama series in which poems used by Bröyer meet contemporary poetry and influences from her movement language are integrated into contemporary dance. Venues: Helsinki City Museum and Burgher’s House Museum