












images that haunt us
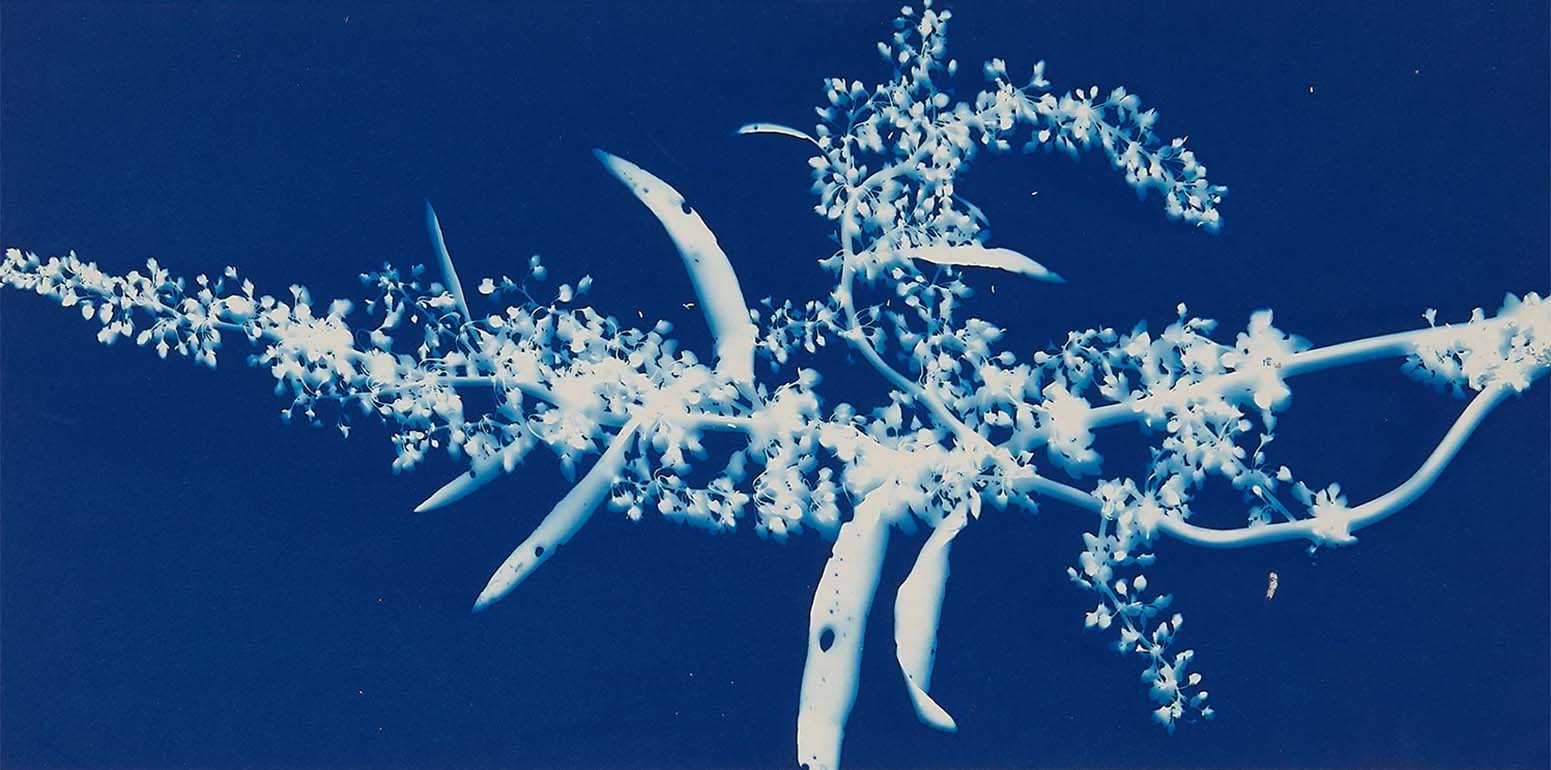
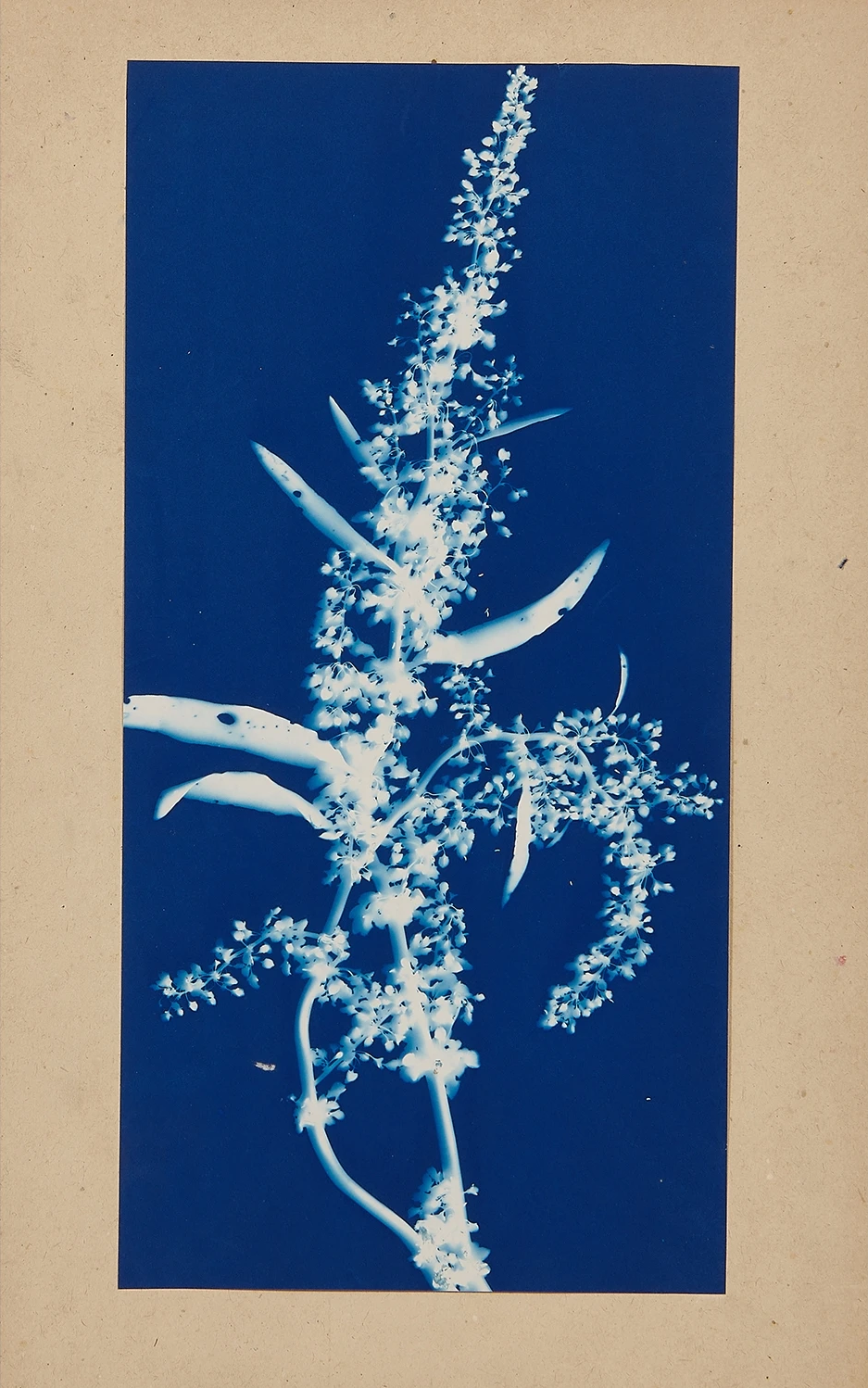



















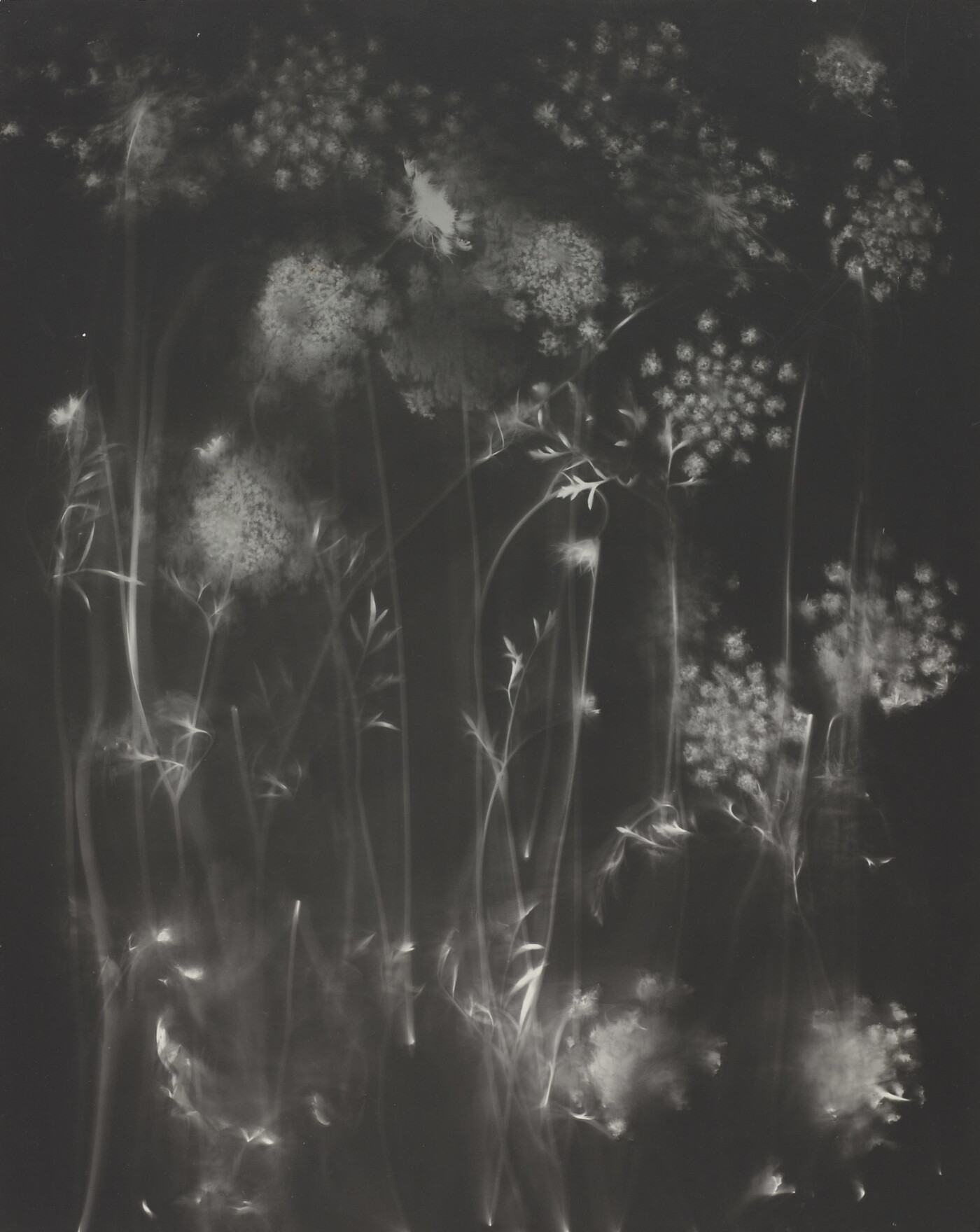
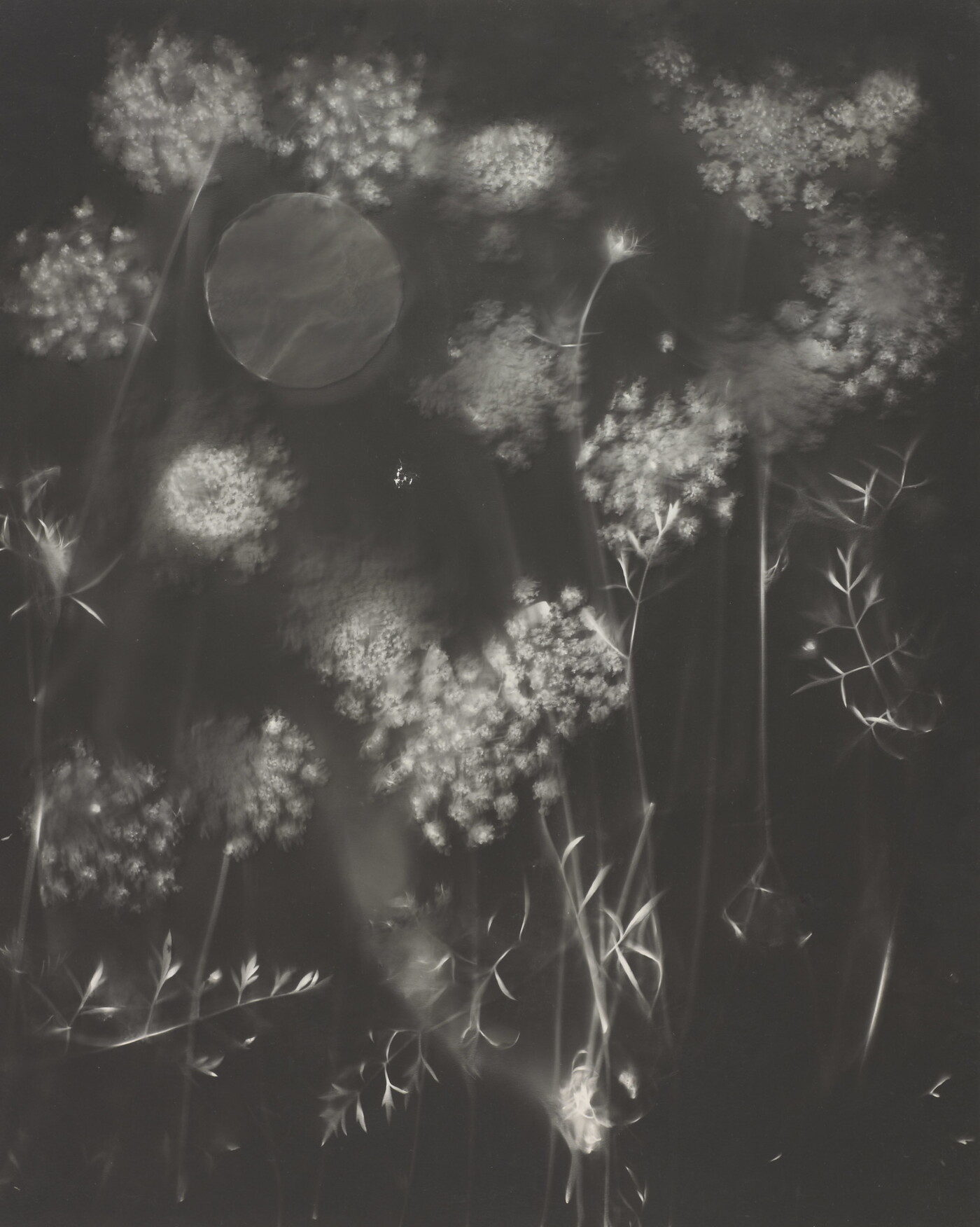
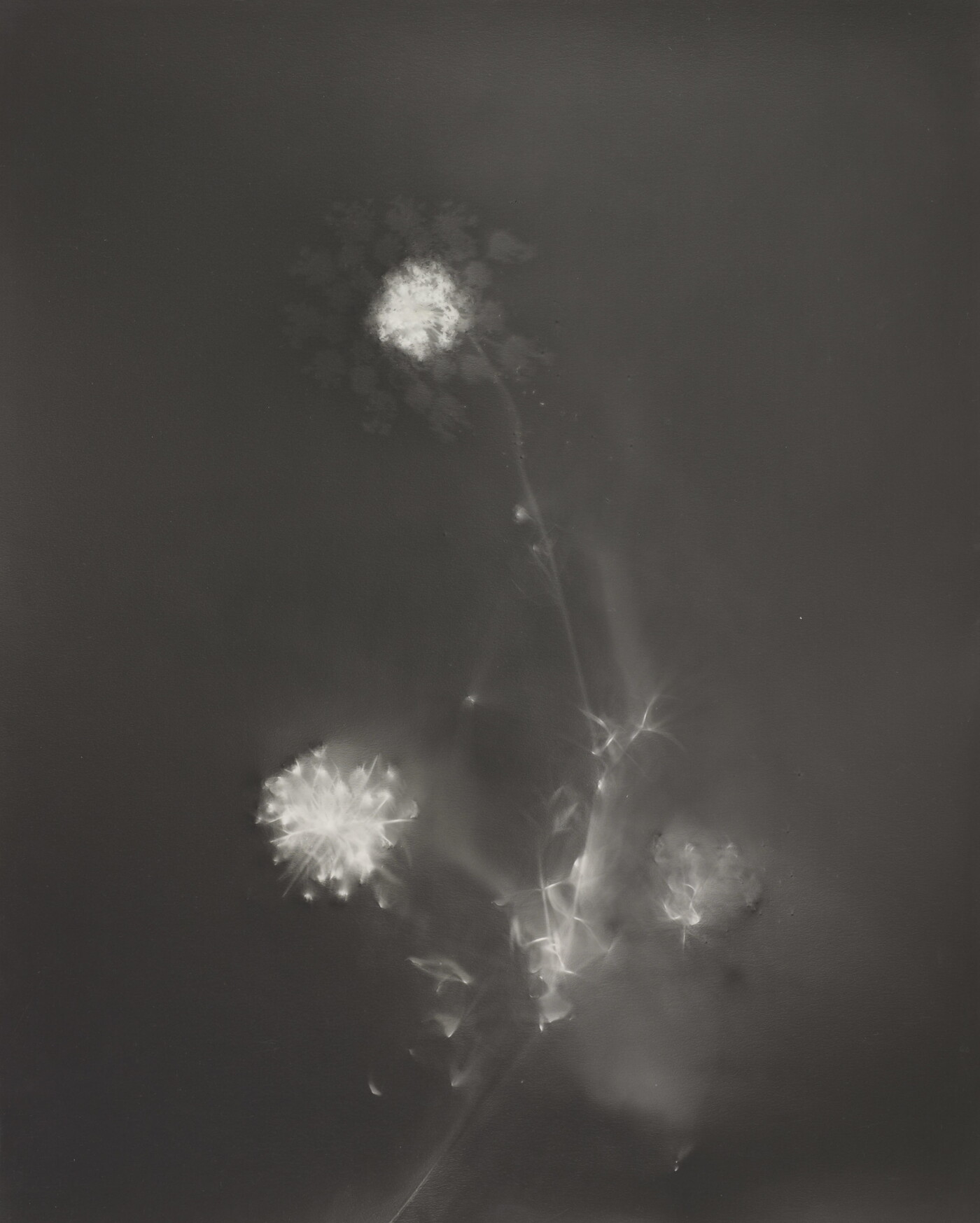
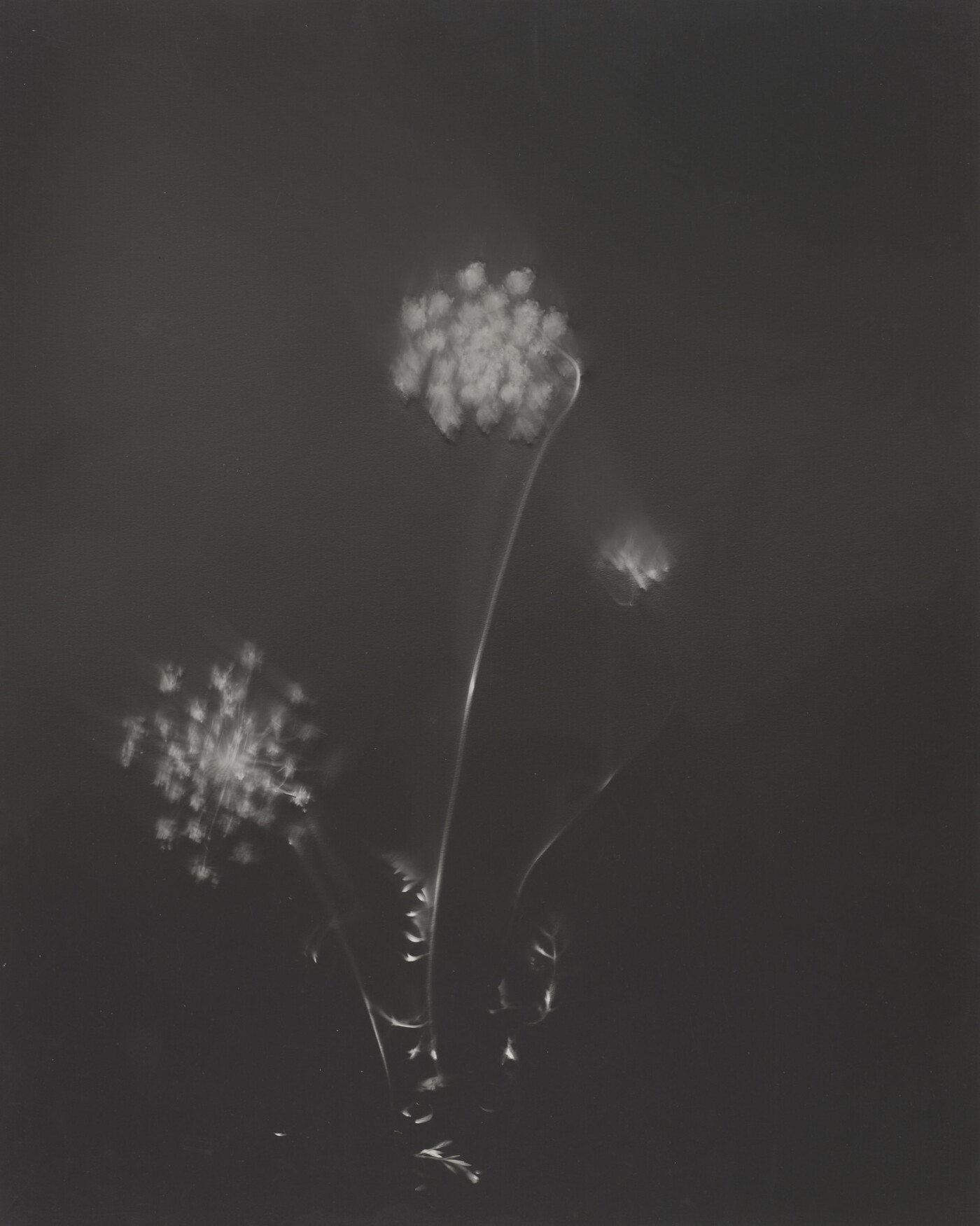
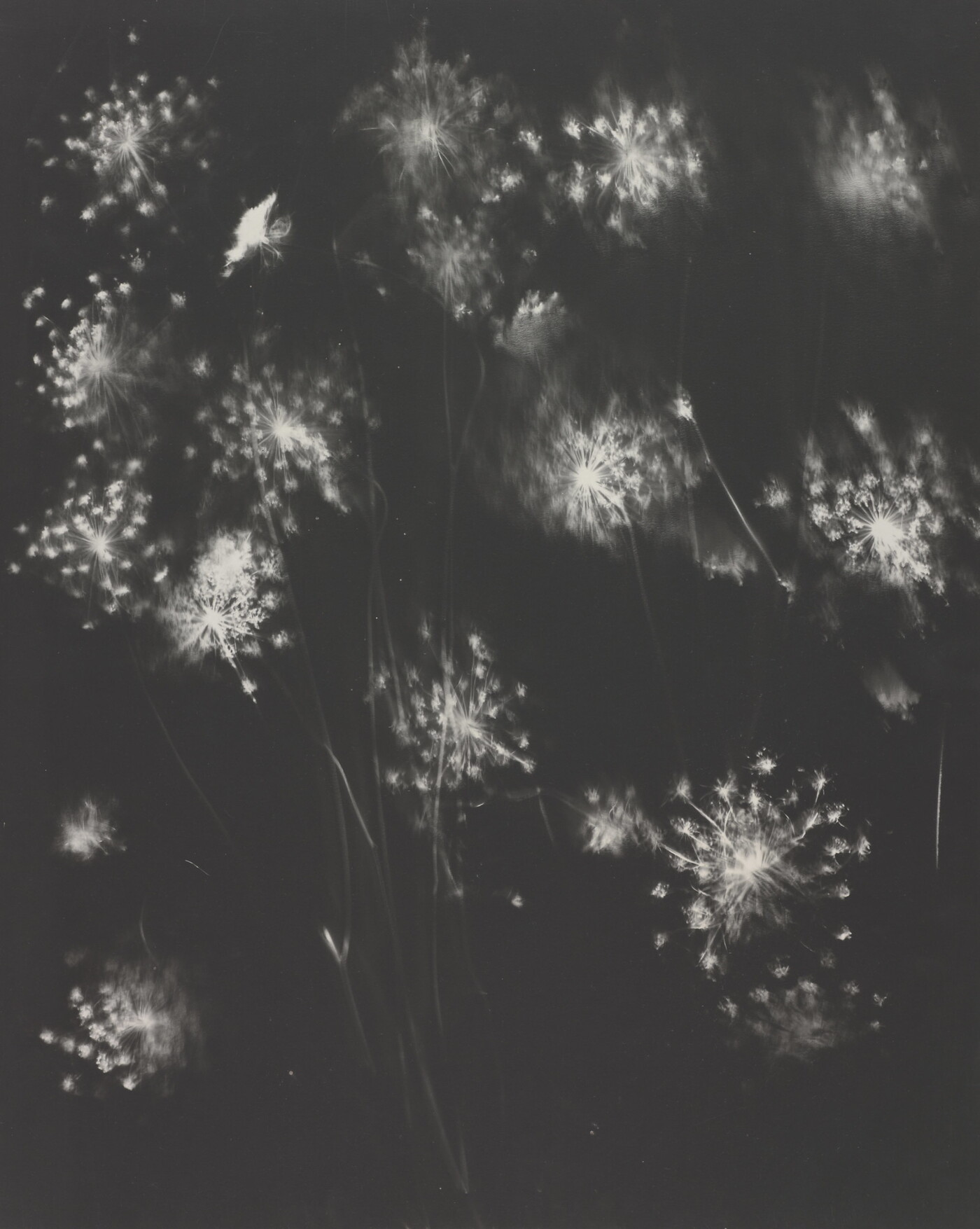
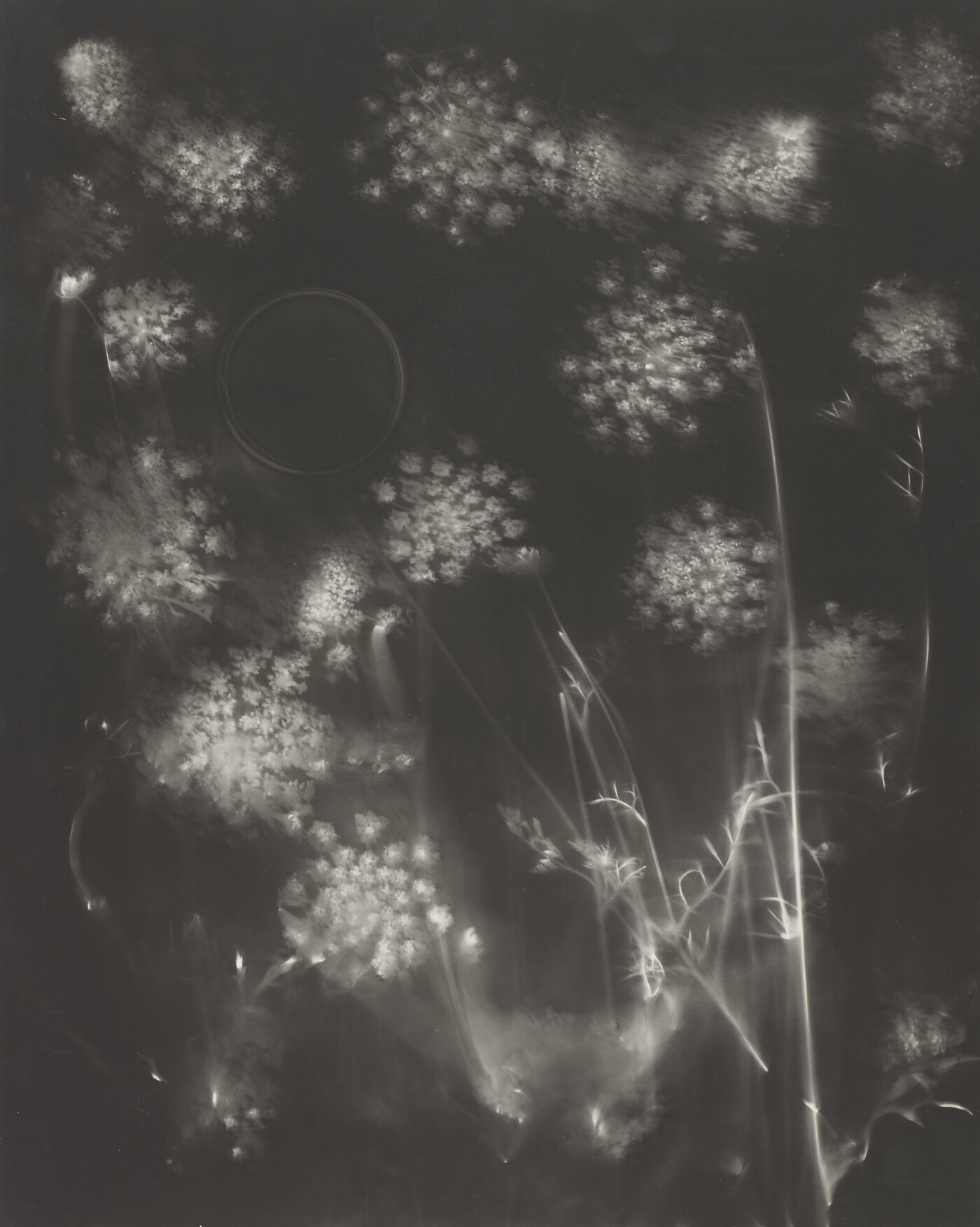
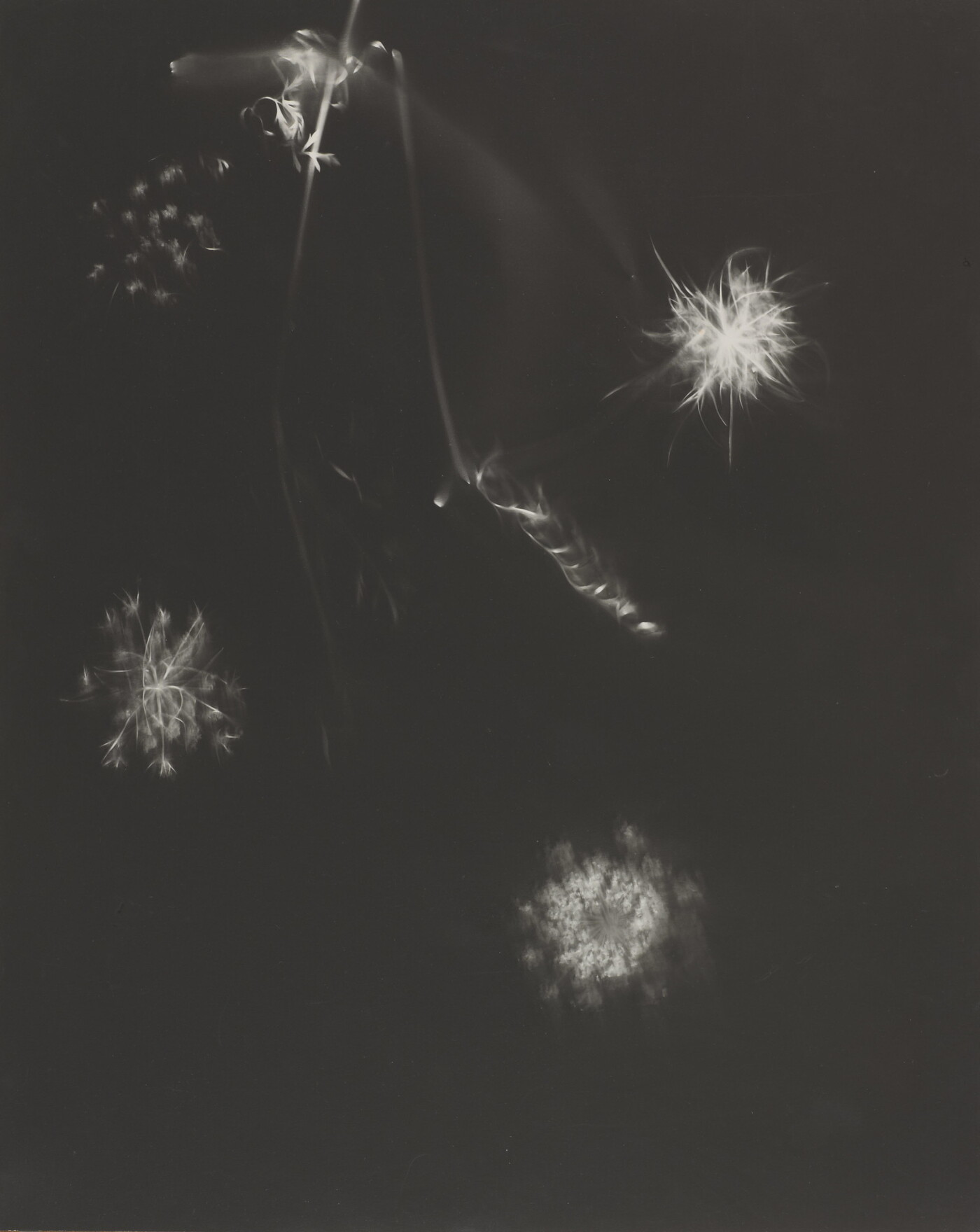
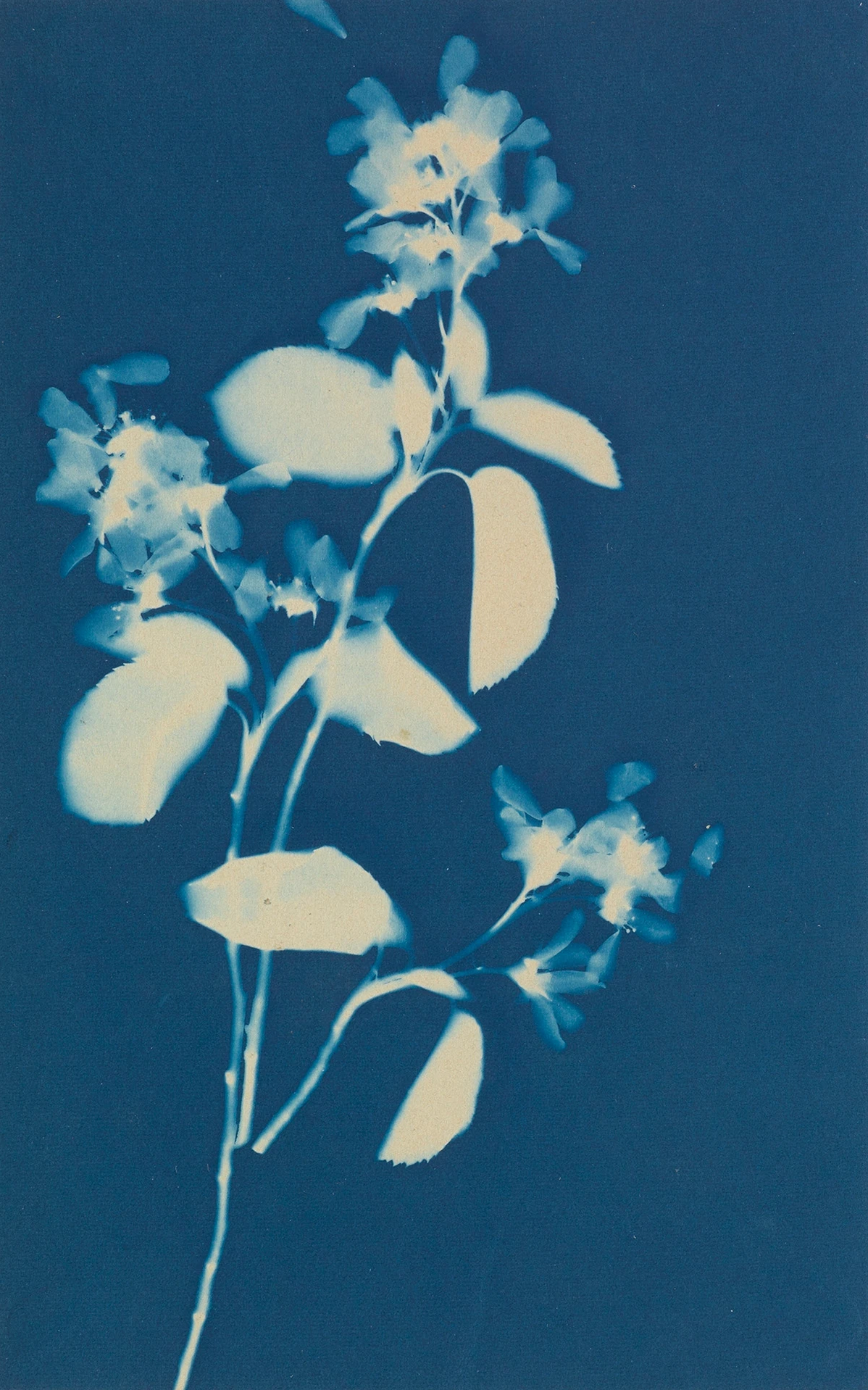
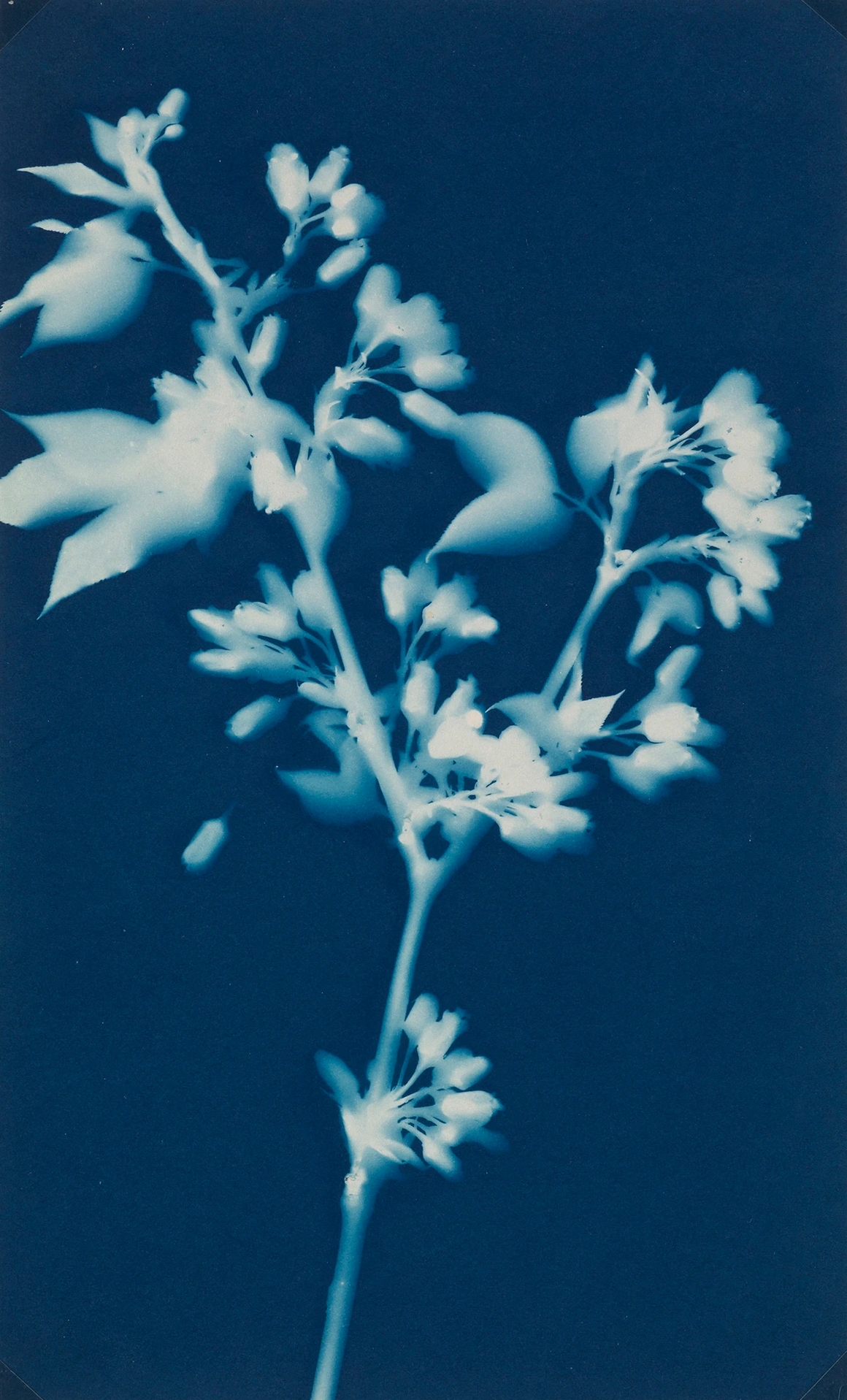
Jaques was already a respected printmaker when she began making cyanotype photograms of wildflowers. An active member of the Wild Flower Preservation Society, she created over a thousand of these botanical images. Made without a camera by placing objects directly on sensitized paper and exposing it to light, the photogram is the least industrialized type of photography. Because prints were easy to produce by this method, it achieved wide popularity. Graphic artists often chose this form of print because of its rich Prussian blue color. Aligned with the antimodernist views of the late Victorian Arts and Crafts movement, Jaques’s work reflects a reverence for commonplace elements of nature and the beautifully crafted object.
Merry A. Foresta American Photographs: The First Century (Washington, D.C.: National Museum of American Art with the Smithsonian Institution Press, 1996). From Smithsonian American Art Museum (SAAM)
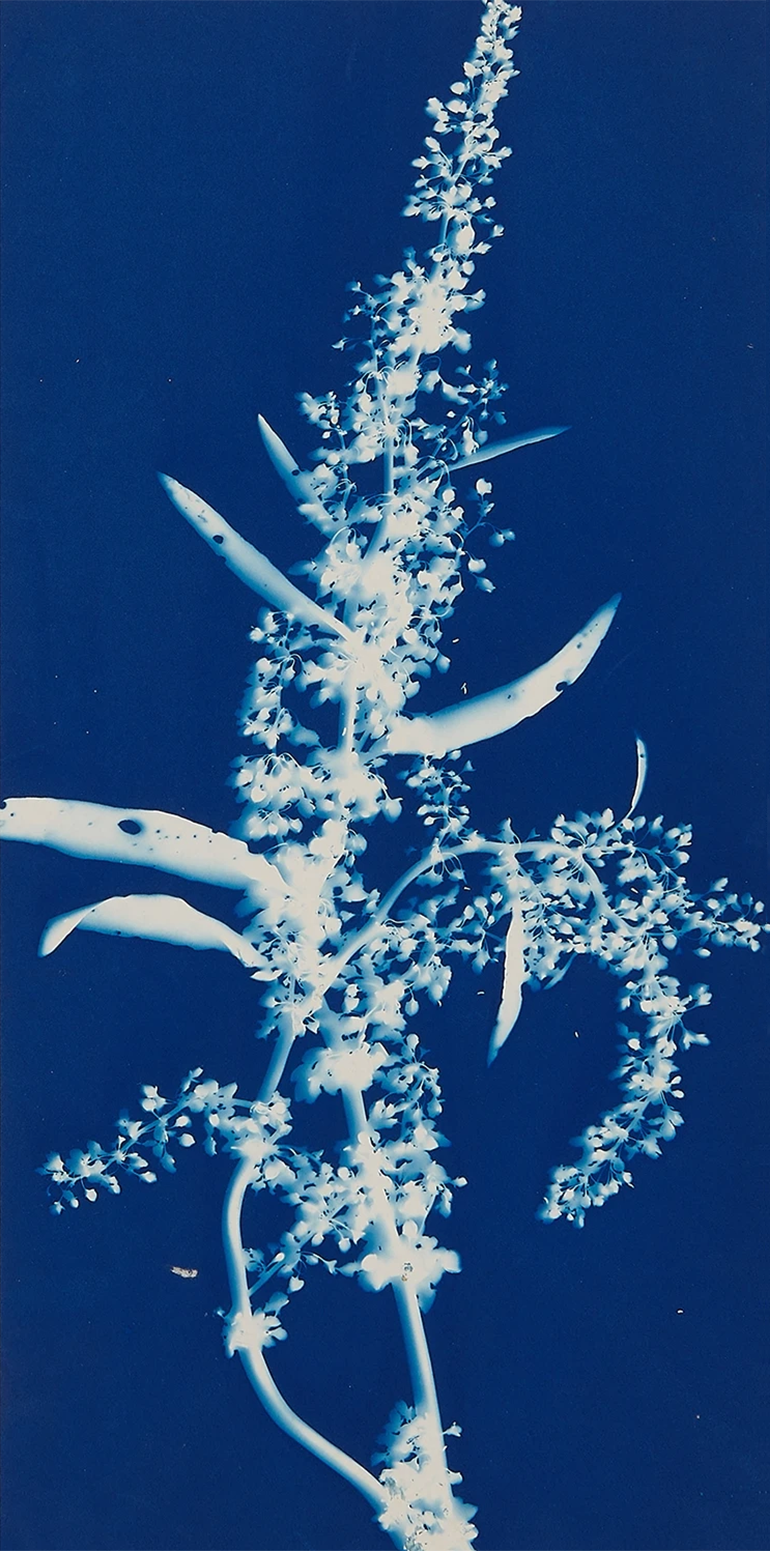
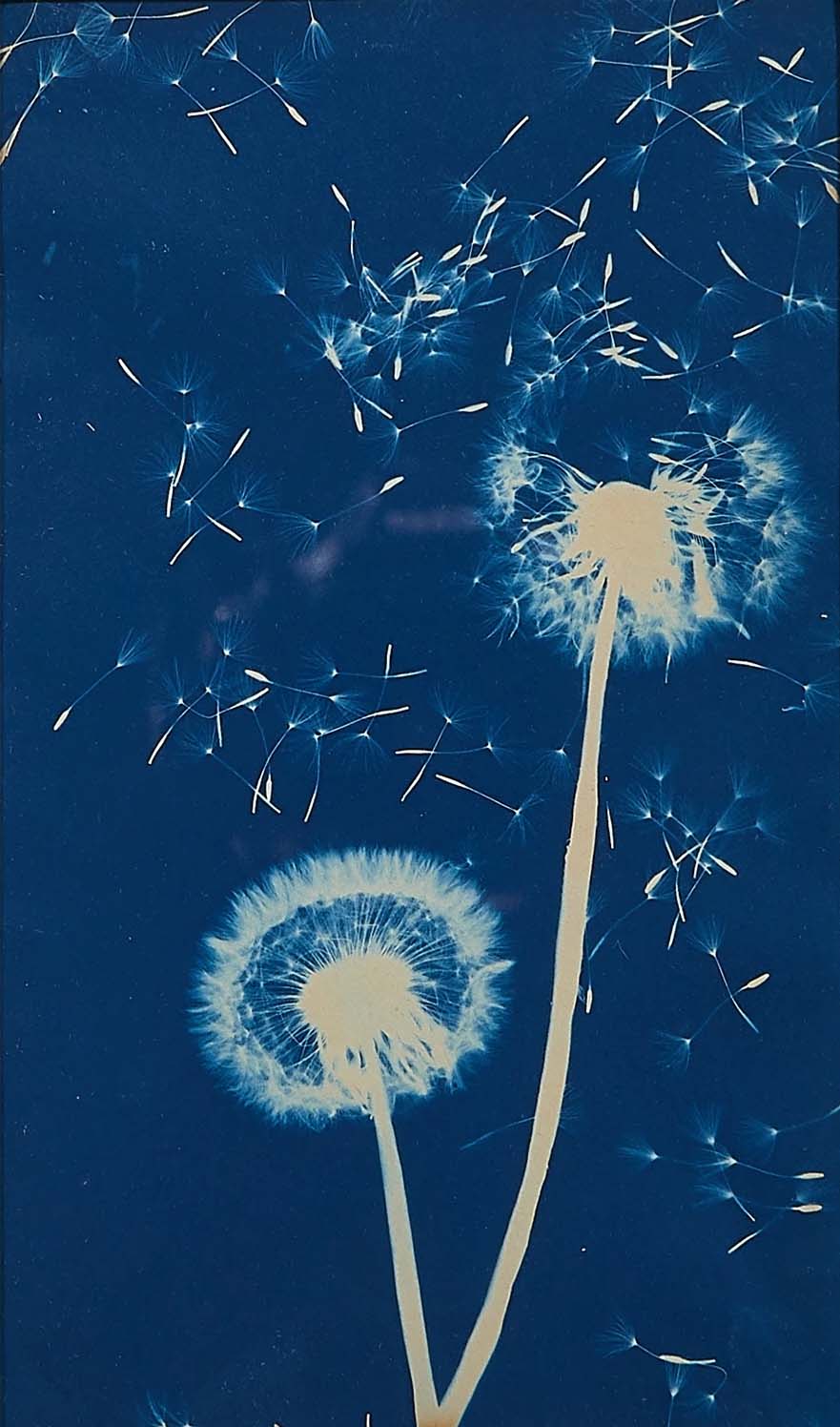

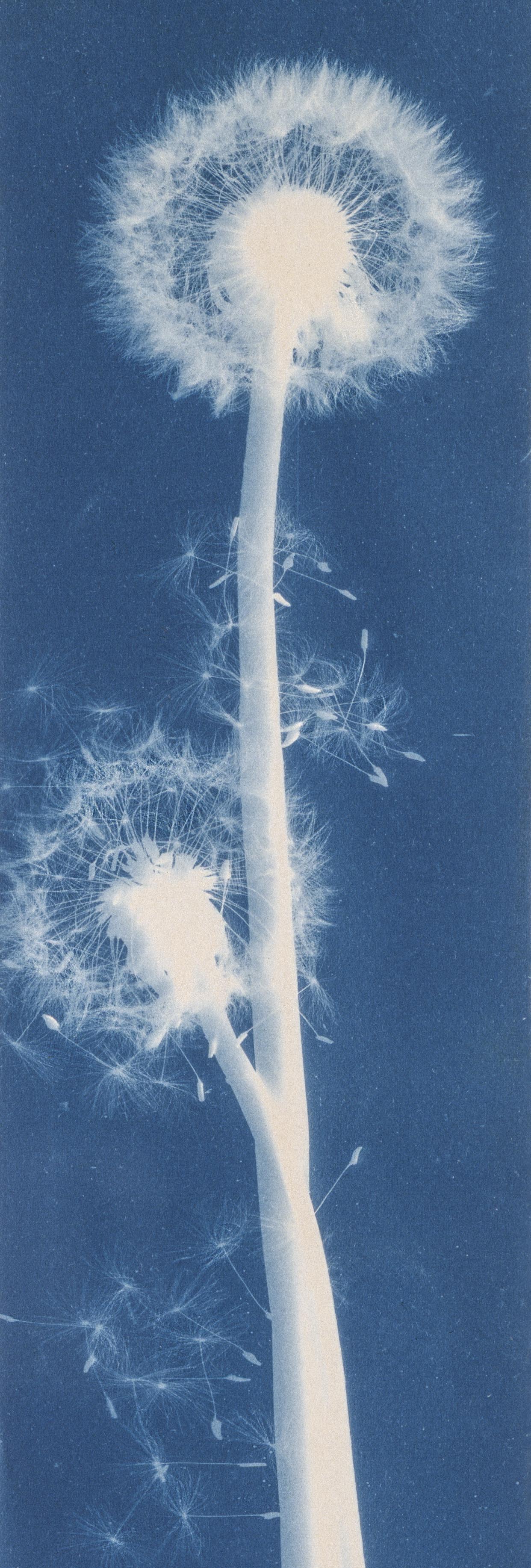

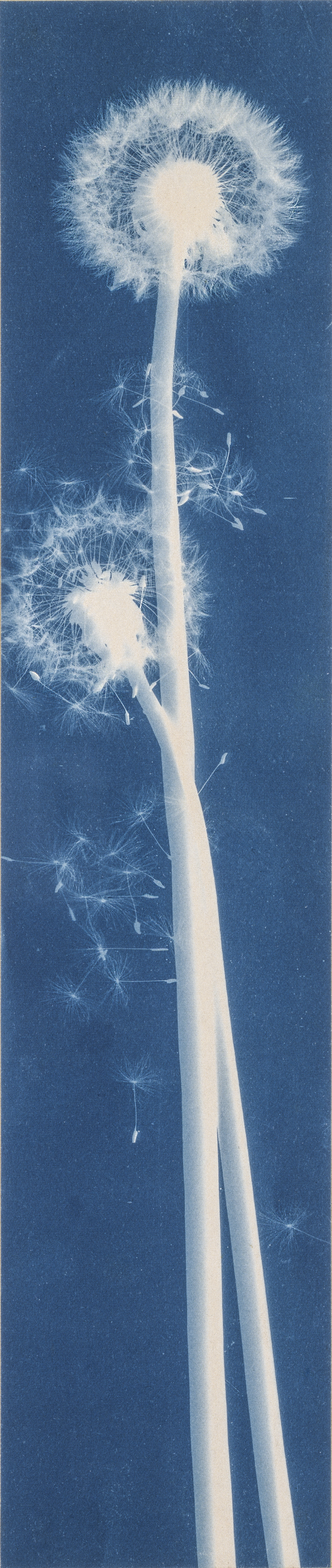
Jaques was already a respected printmaker when she began making cyanotype photograms of wildflowers. An active member of the Wild Flower Preservation Society, she created over a thousand of these botanical images. [See Dandelion Seeds, Taraxacium Officinale, SAAM, 1994.91.89] Made without a camera by placing objects directly on sensitized paper and exposing it to light, the photogram is the least industrialized type of photography. Because prints were easy to produce by this method, it achieved wide popularity. Graphic artists often chose this form of print because of its rich Prussian blue color. Aligned with the antimodernist views of the late Victorian Arts and Crafts movement, Jaques’s work reflects a reverence for commonplace elements of nature and the beautifully crafted object.
Merry A. Foresta American Photographs: The First Century (Washington, D.C.: National Museum of American Art with the Smithsonian Institution Press, 1996). From Smithsonian American Art Museum (SAAM)







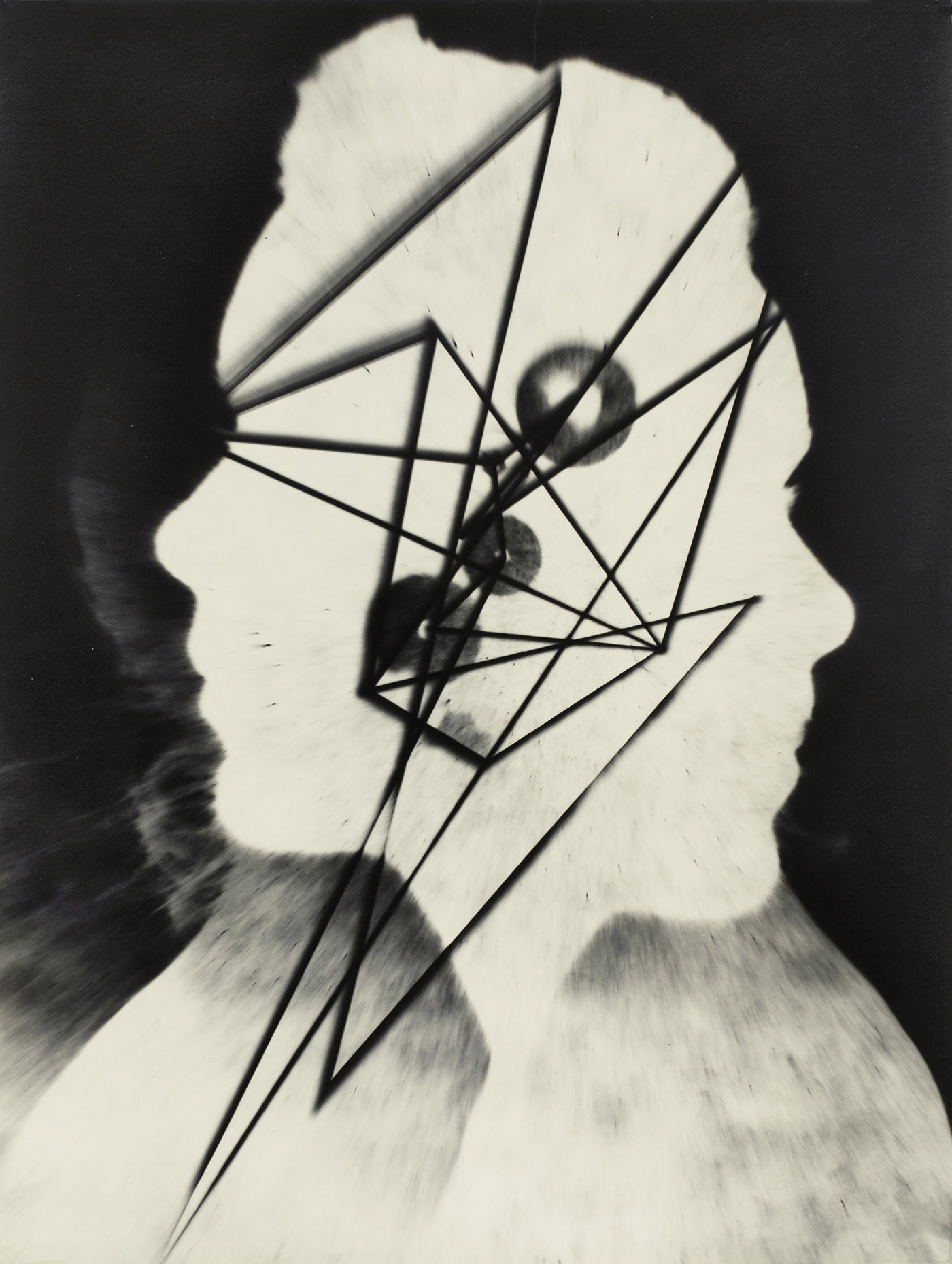
Nude figure of a young woman covered by an inverted glass, which becomes her garment. The translucent glass allows the curves of her figure to be seen, but it still provides a modest covering. The shape of the glass is reminiscent of dress styles of the mid-1800s, with a wide hooped skirt and narrow waistline. Rosa Rolanda painted self-portraits from 1945 and 1952 depict the same somber persona. The simple style of her features is similar to those found on folkloric images of the sun reproduced in ceramics, wood, and textiles. Here, crowned by the sun, she is surrounded by shells, a deer, and a ruler.