


images that haunt us












“My life is full of mistakes. They’re like pebbles that make a good road.” ~ Beatrice Wood

“There are three things important in life:
Honesty, which means living free of the cunning mind.
Compassion, because if we have no concern for others, we are monsters.
Curiosity, for if the mind is not searching, it is dull and unresponsive.”
~ Beatrice Wood
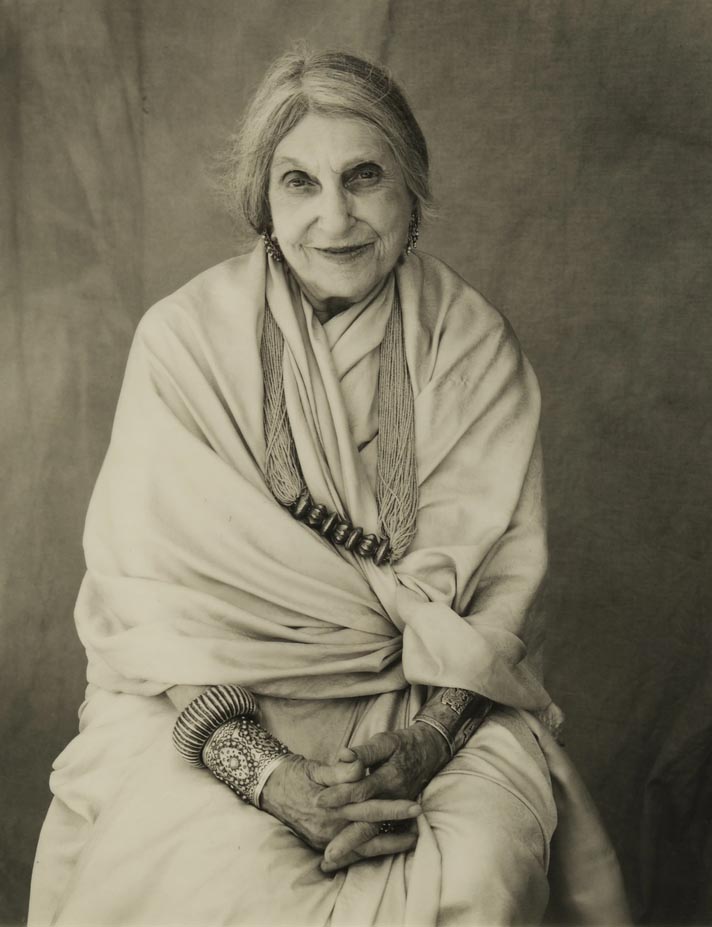

Beatrice Wood, aka the “Mama of Dada” was born into a wealthy San Francisco family in 1893. Defying her family’s Victorian values, she moved to France to study theater and art. On the brink of WWI, her parents brought a reluctant Beatrice back to New York, where her mother did everything within her power to discourage her plans for a career on the New York stage. Despite this, Beatrice’s fluency in French led her to join the French National Repertory Theater, where she played over sixty ingénue roles under the stage name “Mademoiselle Patricia” to save her family’s name and reputation.
Wood’s involvement in the Avant-Garde began in these years with her introduction to Marcel Duchamp and later to his friend Henri-Pierre Roché, a diplomat, writer and art collector. Roché, a man fourteen years her senior, joined the duo, becoming creatively (and romantically) entangled. Together they wrote and edited The Blind Man (and the Rongwrong magazine), a magazine that poked the conservative art establishment and helped define the Dada art movement.
Marcel Duchamp brought Beatrice into the world of the New York Dada group, which existed by the patronage of art collectors Walter and Louise Arensberg. The Arensbergs’ home became the center of legendary soirees that included leading figures of the time including Francis Picabia, Mina Loy, Man Ray, Charles Demuth, Joseph Stella, Charles Sheeler and the composer Edgard Varèse.
Beatrice Wood’s career as an artist of note began when she created an abstraction to tease Duchamp that anyone could create modern art. Duchamp was impressed by the work, arranging to have it published in a magazine and inviting her to work in his studio. It was here that she developed her style of spontaneous sketching and painting that continued throughout her life.
Following the formation of the Society of Independent Artists in 1917, Beatrice exhibited work in their Independents exhibition. [text extracted from Wikipedia entry and Beatrice Wood Center for the Arts]
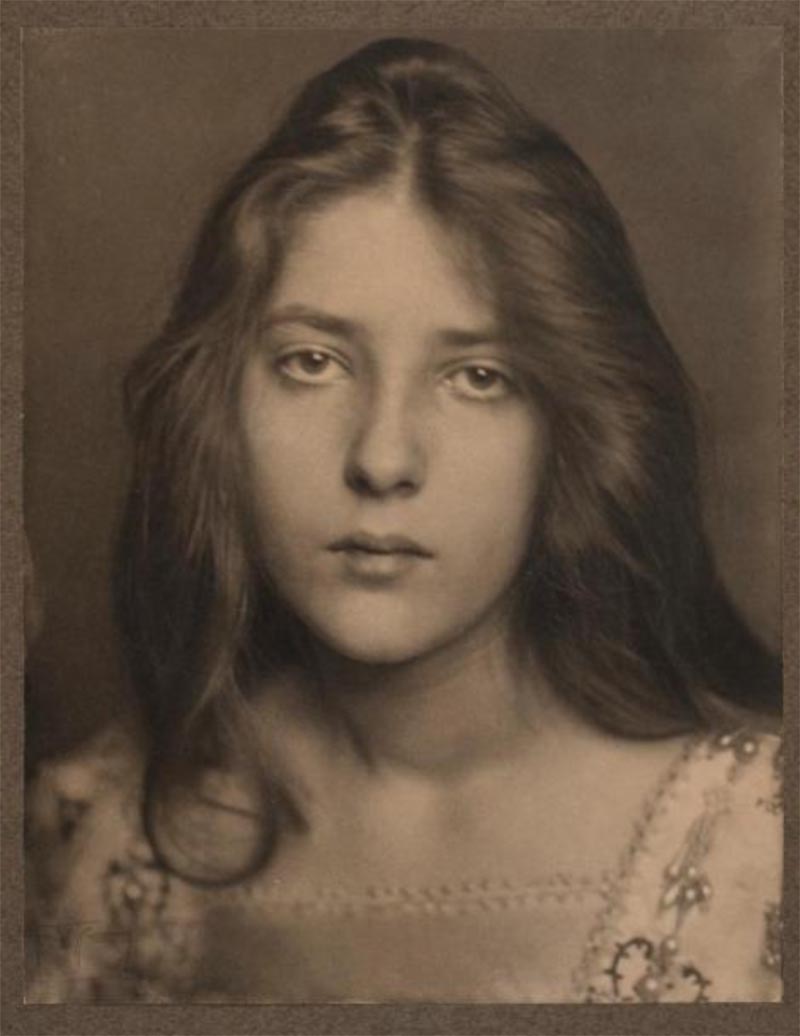
![Eva Watson-Schütze :: [Portrait of an unknown woman among hollyhocks], ca. 1910. [detail] | src Rijksmuseum](https://unregardoblique.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/eva-watson-schutze-woman-by-hollyhocks-ca.-1915-detail.jpg)
![Eva Watson-Schütze :: Portret van een onbekend meisje tussen bloemen [Unknown woman among hollyhocks], ca. 1910. Gelatin silver print on baryta paper. [Public domain] | src Rijksmuseum](https://live.staticflickr.com/65535/52261035754_8a49b570fd_o.jpg)






Eva Watson-Schütze (born, Eva Lawrence Watson) (1867–1935)
In 1883, when Eva Watson was sixteen, she enrolled in the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts in Philadelphia, where she studied under well-known painter and photographer Thomas Eakins. Her interests at that time were watercolor and oil painting, and it’s unknown if she took any interests in Eakins’ photography.
Around the 1890s Watson began to develop a passion for photography, and soon she decided to make it her career. Between 1894 and 1896 she shared a photographic studio with Amelia Van Buren, another Academy alumna, in Philadelphia, and the following year she opened her own portrait studio. She quickly became known for her pictorialist style, and soon her studio was known as a gathering place for photographers who championed this aesthetic vision.
In 1897 she wrote to photographer Frances Benjamin Johnston about her belief in women’s future in photography: “There will be a new era, and women will fly into photography.”
In 1898 six of her photographs were chosen to be exhibited at the first Philadelphia Photographic Salon, where she exhibited under the name Eva Lawrence Watson. It was through this exhibition that she became acquainted with Alfred Stieglitz, who was one of the judges for the exhibit.
In 1899 she was elected as a member of the Photographic Society of Philadelphia. Photographer and critic Joseph Keiley praised the work she exhibited that year, saying she showed “delicate taste and artistic originality”.
The following year she was a member of the jury for the Philadelphia Photographic Salon. A sign of her stature as a photographer at that time may be seen by looking at the other members of the jury, who were Alfred Stieglitz, Gertrude Kasebier, Frank Eugene and Clarence H. White.
In 1900 Johnston asked her to submit work for a groundbreaking exhibition of American women photographers in Paris. Watson objected at first, saying “It has been one of my special hobbies – and one I have been very emphatic about, not to have my work represented as ‘women’s work’. I want [my work] judged by only one standard irrespective of sex.” Johnston persisted, however, and Watson had twelve prints – the largest number of any photographer – in the show that took place in 1901.
In 1901 she married Professor Martin Schütze, a German-born trained lawyer who had received his Ph.D. in German literature from the University of Pennsylvania in 1899. He took a teaching position in Chicago, where the couple soon moved.
That same year she was elected a member of The Linked Ring. She found the ability to correspond with some of the most progressive photographers of the day very invigorating, and she began to look for similar connections in the U.S.
In 1902 she suggested the idea of forming an association of independent and like-minded photographers to Alfred Stieglitz. They corresponded several times about this idea, and by the end of the year she joined Stieglitz as one of the founding members of the famous Photo-Secession.
Since Watson-Schütze’s death there have been two retrospective exhibitions of her photographs: Eva Watson-Schütze, Chicago Photo-Secessionist, at the University of Chicago Library in 1985, and Eva Watson-Schütze, Photographer, at the Samuel Dorsky Museum Art at the State University of New York at New Paltz in 2009.
Her works were also included in exhibits at the National Museum of Women in the Arts in Washington, DC. [quoted from Wikipedia website]